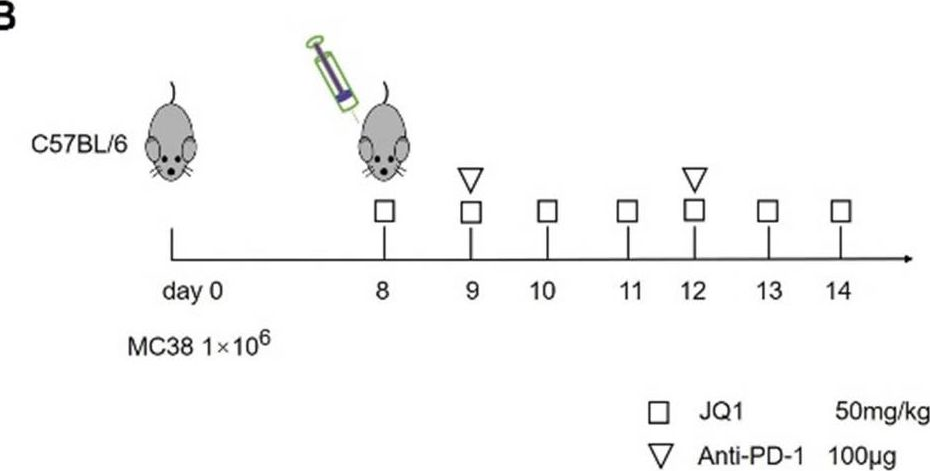
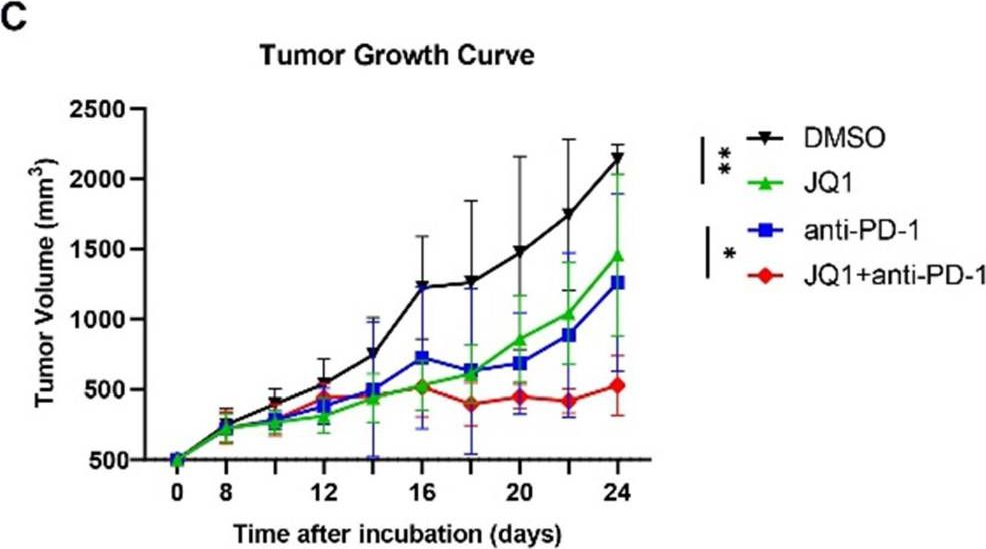
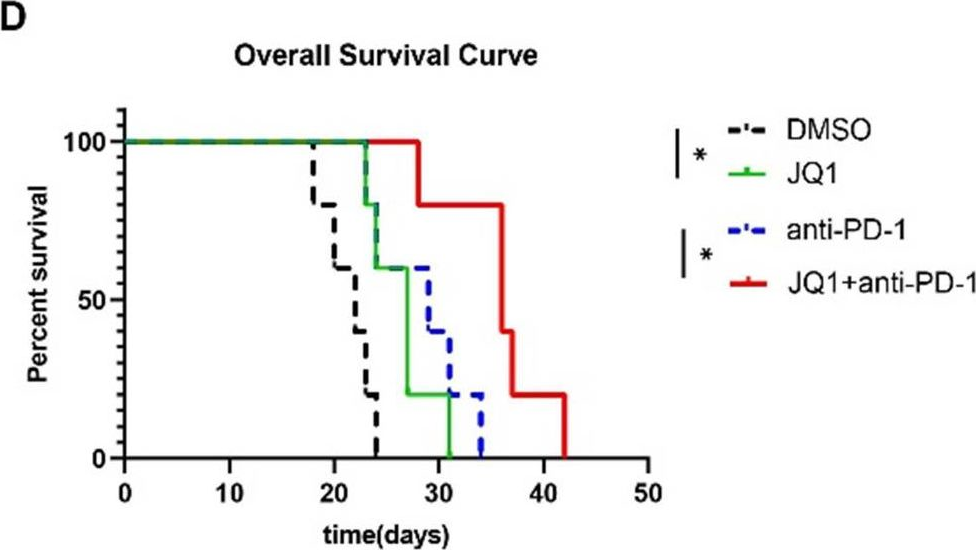
InVivoPlus anti-mouse PD-1 (CD279)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoPlus rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Syrian Hamster BKH cells transfected with mouse PD-1 cDNA |
| Reported Applications | in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signalingin vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin* |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Aggregation* | <5%, Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10949053 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests* |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Nakazawa Y, Miyano M, Tsukamoto S, Kogai H, Yamamoto A, Iso K, Inoue S, Yamane Y, Yabe Y, Umihara H, Taguchi J, Akagi T, Yamaguchi A, Koga M, Toshimitsu K, Hirayama T, Mukai Y, Machinaga A (2024). "Delivery of a BET protein degrader via a CEACAM6-tar
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has the worst prognosis of all cancers. To improve PDAC therapy, we establish screening systems based on organoid and co-culture technologies and find a payload of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), a bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) protein degrader named EBET. We select CEACAM6/CD66c as an ADC target and developed an antibody, #84.7, with minimal reactivity to CEACAM6-expressing normal cells. EBET-conjugated #84.7 (84-EBET) has lethal effects on various PDAC organoids and bystander efficacy on CEACAM6-negative PDAC cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. In mouse studies, a single injection of 84-EBET induces marked tumor regression in various PDAC-patient-derived xenografts, with a decrease in the inflammatory phenotype of stromal cells and without significant body weight loss. Combination with standard chemotherapy or PD-1 antibody induces more profound and sustained regression without toxicity enhancement. Our preclinical evidence demonstrates potential efficacy by delivering BET protein degrader to PDAC and its microenvironment via CEACAM6-targeted ADC.
in vivo macrophage depletion
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo NK cell depletion
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
in vivo neutrophil depletion
in vivo eosinophil depletion
Moynihan, K. D., et al (2016). "Eradication of large established tumors in mice by combination immunotherapy that engages innate and adaptive immune responses" Nat Med. doi : 10.1038/nm.4200.
PubMed
Checkpoint blockade with antibodies specific for cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein (CTLA)-4 or programmed cell death 1 (PDCD1; also known as PD-1) elicits durable tumor regression in metastatic cancer, but these dramatic responses are confined to a minority of patients. This suboptimal outcome is probably due in part to the complex network of immunosuppressive pathways present in advanced tumors, which are unlikely to be overcome by intervention at a single signaling checkpoint. Here we describe a combination immunotherapy that recruits a variety of innate and adaptive immune cells to eliminate large tumor burdens in syngeneic tumor models and a genetically engineered mouse model of melanoma; to our knowledge tumors of this size have not previously been curable by treatments relying on endogenous immunity. Maximal antitumor efficacy required four components: a tumor-antigen-targeting antibody, a recombinant interleukin-2 with an extended half-life, anti-PD-1 and a powerful T cell vaccine. Depletion experiments revealed that CD8+ T cells, cross-presenting dendritic cells and several other innate immune cell subsets were required for tumor regression. Effective treatment induced infiltration of immune cells and production of inflammatory cytokines in the tumor, enhanced antibody-mediated tumor antigen uptake and promoted antigen spreading. These results demonstrate the capacity of an elicited endogenous immune response to destroy large, established tumors and elucidate essential characteristics of combination immunotherapies that are capable of curing a majority of tumors in experimental settings typically viewed as intractable.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Curran, M. A., et al (2010). "PD-1 and CTLA-4 combination blockade expands infiltrating T cells and reduces regulatory T and myeloid cells within B16 melanoma tumors" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(9): 4275-4280.
PubMed
Vaccination with irradiated B16 melanoma cells expressing either GM-CSF (Gvax) or Flt3-ligand (Fvax) combined with antibody blockade of the negative T-cell costimulatory receptor cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) promotes rejection of preimplanted tumors. Despite CTLA-4 blockade, T-cell proliferation and cytokine production can be inhibited by the interaction of programmed death-1 (PD-1) with its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 or by the interaction of PD-L1 with B7-1. Here, we show that the combination of CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade is more than twice as effective as either alone in promoting the rejection of B16 melanomas in conjunction with Fvax. Adding alphaPD-L1 to this regimen results in rejection of 65% of preimplanted tumors vs. 10% with CTLA-4 blockade alone. Combination PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade increases effector T-cell (Teff) infiltration, resulting in highly advantageous Teff-to-regulatory T-cell ratios with the tumor. The fraction of tumor-infiltrating Teffs expressing CTLA-4 and PD-1 increases, reflecting the proliferation and accumulation of cells that would otherwise be anergized. Combination blockade also synergistically increases Teff-to-myeloid-derived suppressor cell ratios within B16 melanomas. IFN-gamma production increases in both the tumor and vaccine draining lymph nodes, as does the frequency of IFN-gamma/TNF-alpha double-producing CD8(+) T cells within the tumor. These results suggest that combination blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1- and CTLA-4-negative costimulatory pathways allows tumor-specific T cells that would otherwise be inactivated to continue to expand and carry out effector functions, thereby shifting the tumor microenvironment from suppressive to inflammatory.
in vivo TIM-3 neutralization
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Flow Cytometry
Ngiow, S. F., et al (2015). "A Threshold Level of Intratumor CD8+ T-cell PD1 Expression Dictates Therapeutic Response to Anti-PD1" Cancer Res 75(18): 3800-3811.
PubMed
Despite successes, thus far, a significant proportion of the patients treated with anti-PD1 antibodies have failed to respond. We use mouse tumor models of anti-PD1 sensitivity and resistance and flow cytometry to assess tumor-infiltrating immune cells immediately after therapy. We demonstrate that the expression levels of T-cell PD1 (PD1(lo)), myeloid, and T-cell PDL1 (PDL1(hi)) in the tumor microenvironment inversely correlate and dictate the efficacy of anti-PD1 mAb and function of intratumor CD8(+) T cells. In sensitive tumors, we reveal a threshold for PD1 downregulation on tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T cells below which the release of adaptive immune resistance is achieved. In contrast, PD1(hi) T cells in resistant tumors fail to be rescued by anti-PD1 therapy and remain dysfunctional unless intratumor PDL1(lo) immune cells are targeted. Intratumor Tregs are partly responsible for the development of anti-PD1-resistant tumors and PD1(hi) CD8(+) T cells. Our analyses provide a framework to interrogate intratumor CD8(+) T-cell PD1 and immune PDL1 levels and response in human cancer. Cancer Res; 75(18); 3800-11. (c)2015 AACR.
in vivo TIM-3 neutralization
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo LAG-3 neutralization
McGray, A. J., et al (2014). "Immunotherapy-induced CD8+ T cells instigate immune suppression in the tumor" Mol Ther 22(1): 206-218.
PubMed
Despite clear evidence of immunogenicity, cancer vaccines only provide a modest clinical benefit. To evaluate the mechanisms that limit tumor regression following vaccination, we have investigated the weak efficacy of a highly immunogenic experimental vaccine using a murine melanoma model. We discovered that the tumor adapts rapidly to the immune attack instigated by tumor-specific CD8+ T cells in the first few days following vaccination, resulting in the upregulation of a complex set of biological networks, including multiple immunosuppressive processes. This rapid adaptation acts to prevent sustained local immune attack, despite continued infiltration by increasing numbers of tumor-specific T cells. Combining vaccination with adoptive transfer of tumor-specific T cells produced complete regression of the treated tumors but did not prevent the adaptive immunosuppression. In fact, the adaptive immunosuppressive pathways were more highly induced in regressing tumors, commensurate with the enhanced level of immune attack. Examination of tumor infiltrating T-cell functionality revealed that the adaptive immunosuppression leads to a progressive loss in T-cell function, even in tumors that are regressing. These novel observations that T cells produced by therapeutic intervention can instigate a rapid adaptive immunosuppressive response within the tumor have important implications for clinical implementation of immunotherapies.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Grasselly, C., et al (2018). "The Antitumor Activity of Combinations of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Is Model-Dependent" Front Immunol 9: 2100.
PubMed
In spite of impressive response rates in multiple cancer types, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are active in only a minority of patients. Alternative strategies currently aim to combine immunotherapies with conventional agents such as cytotoxic chemotherapies. Here, we performed a study of PD-1 or PDL-1 blockade in combination with reference chemotherapies in four fully immunocompetent mouse models of cancer. We analyzed both the in vivo antitumor response, and the tumor immune infiltrate 4 days after the first treatment. in vivo tumor growth experiments revealed variable responsiveness to ICIs between models. We observed enhanced antitumor effects of the combination of immunotherapy with chemotherapy in the MC38 colon and MB49 bladder models, a lack of response in the 4T1 breast model, and an inhibition of ICIs activity in the MBT-2 bladder model. Flow cytometry analysis of tumor samples showed significant differences in all models between untreated and treated mice. At baseline, all the tumor models studied were predominantly infiltrated with cells harboring an immunosuppressive phenotype. Early alterations of the tumor immune infiltrate after treatment were found to be highly variable. We found that the balance between effector cells and immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment could be altered with some treatment combinations, but this effect was not always correlated with an impact on in vivo tumor growth. These results show that the combination of cytotoxic chemotherapy with ICIs may result in enhanced, similar or reduced antitumor activity, in a model- and regimen-dependent fashion. The present investigations should help to select appropriate combination regimens for ICIs.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Evans, E. E., et al (2015). "Antibody Blockade of Semaphorin 4D Promotes Immune Infiltration into Tumor and Enhances Response to Other Immunomodulatory Therapies" Cancer Immunol Res 3(6): 689-701.
PubMed
Semaphorin 4D (SEMA4D, CD100) and its receptor plexin-B1 (PLXNB1) are broadly expressed in murine and human tumors, and their expression has been shown to correlate with invasive disease in several human tumors. SEMA4D normally functions to regulate the motility and differentiation of multiple cell types, including those of the immune, vascular, and nervous systems. In the setting of cancer, SEMA4D-PLXNB1 interactions have been reported to affect vascular stabilization and transactivation of ERBB2, but effects on immune-cell trafficking in the tumor microenvironment (TME) have not been investigated. We describe a novel immunomodulatory function of SEMA4D, whereby strong expression of SEMA4D at the invasive margins of actively growing tumors influences the infiltration and distribution of leukocytes in the TME. Antibody neutralization of SEMA4D disrupts this gradient of expression, enhances recruitment of activated monocytes and lymphocytes into the tumor, and shifts the balance of cells and cytokines toward a proinflammatory and antitumor milieu within the TME. This orchestrated change in the tumor architecture was associated with durable tumor rejection in murine Colon26 and ERBB2(+) mammary carcinoma models. The immunomodulatory activity of anti-SEMA4D antibody can be enhanced by combination with other immunotherapies, including immune checkpoint inhibition and chemotherapy. Strikingly, the combination of anti-SEMA4D antibody with antibody to CTLA-4 acts synergistically to promote complete tumor rejection and survival. Inhibition of SEMA4D represents a novel mechanism and therapeutic strategy to promote functional immune infiltration into the TME and inhibit tumor progression.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Twyman-Saint Victor, C., et al (2015). "Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer" Nature 520(7547): 373-377.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors result in impressive clinical responses, but optimal results will require combination with each other and other therapies. This raises fundamental questions about mechanisms of non-redundancy and resistance. Here we report major tumour regressions in a subset of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with an anti-CTLA4 antibody (anti-CTLA4) and radiation, and reproduced this effect in mouse models. Although combined treatment improved responses in irradiated and unirradiated tumours, resistance was common. Unbiased analyses of mice revealed that resistance was due to upregulation of PD-L1 on melanoma cells and associated with T-cell exhaustion. Accordingly, optimal response in melanoma and other cancer types requires radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1/PD-1. Anti-CTLA4 predominantly inhibits T-regulatory cells (Treg cells), thereby increasing the CD8 T-cell to Treg (CD8/Treg) ratio. Radiation enhances the diversity of the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire of intratumoral T cells. Together, anti-CTLA4 promotes expansion of T cells, while radiation shapes the TCR repertoire of the expanded peripheral clones. Addition of PD-L1 blockade reverses T-cell exhaustion to mitigate depression in the CD8/Treg ratio and further encourages oligoclonal T-cell expansion. Similarly to results from mice, patients on our clinical trial with melanoma showing high PD-L1 did not respond to radiation plus anti-CTLA4, demonstrated persistent T-cell exhaustion, and rapidly progressed. Thus, PD-L1 on melanoma cells allows tumours to escape anti-CTLA4-based therapy, and the combination of radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1 promotes response and immunity through distinct mechanisms.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Vanpouille-Box, C., et al (2015). "TGFbeta Is a Master Regulator of Radiation Therapy-Induced Antitumor Immunity" Cancer Res 75(11): 2232-2242.
PubMed
T cells directed to endogenous tumor antigens are powerful mediators of tumor regression. Recent immunotherapy advances have identified effective interventions to unleash tumor-specific T-cell activity in patients who naturally develop them. Eliciting T-cell responses to a patient’s individual tumor remains a major challenge. Radiation therapy can induce immune responses to model antigens expressed by tumors, but it remains unclear whether it can effectively prime T cells specific for endogenous antigens expressed by poorly immunogenic tumors. We hypothesized that TGFbeta activity is a major obstacle hindering the ability of radiation to generate an in situ tumor vaccine. Here, we show that antibody-mediated TGFbeta neutralization during radiation therapy effectively generates CD8(+) T-cell responses to multiple endogenous tumor antigens in poorly immunogenic mouse carcinomas. Generated T cells were effective at causing regression of irradiated tumors and nonirradiated lung metastases or synchronous tumors (abscopal effect). Gene signatures associated with IFNgamma and immune-mediated rejection were detected in tumors treated with radiation therapy and TGFbeta blockade in combination but not as single agents. Upregulation of programmed death (PD) ligand-1 and -2 in neoplastic and myeloid cells and PD-1 on intratumoral T cells limited tumor rejection, resulting in rapid recurrence. Addition of anti-PD-1 antibodies extended survival achieved with radiation and TGFbeta blockade. Thus, TGFbeta is a fundamental regulator of radiation therapy’s ability to generate an in situ tumor vaccine. The combination of local radiation therapy with TGFbeta neutralization offers a novel individualized strategy for vaccinating patients against their tumors.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Zelenay, S., et al (2015). "Cyclooxygenase-Dependent Tumor Growth through Evasion of Immunity" Cell 162(6): 1257-1270.
PubMed
The mechanisms by which melanoma and other cancer cells evade anti-tumor immunity remain incompletely understood. Here, we show that the growth of tumors formed by mutant Braf(V600E) mouse melanoma cells in an immunocompetent host requires their production of prostaglandin E2, which suppresses immunity and fuels tumor-promoting inflammation. Genetic ablation of cyclooxygenases (COX) or prostaglandin E synthases in Braf(V600E) mouse melanoma cells, as well as in Nras(G12D) melanoma or in breast or colorectal cancer cells, renders them susceptible to immune control and provokes a shift in the tumor inflammatory profile toward classic anti-cancer immune pathways. This mouse COX-dependent inflammatory signature is remarkably conserved in human cutaneous melanoma biopsies, arguing for COX activity as a driver of immune suppression across species. Pre-clinical data demonstrate that inhibition of COX synergizes with anti-PD-1 blockade in inducing eradication of tumors, implying that COX inhibitors could be useful adjuvants for immune-based therapies in cancer patients.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
John, L. B., et al (2013). "Anti-PD-1 antibody therapy potently enhances the eradication of established tumors by gene-modified T cells" Clin Cancer Res 19(20): 5636-5646.
PubMed
PURPOSE: To determine the antitumor efficacy and toxicity of a novel combination approach involving adoptive T-cell immunotherapy using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells with an immunomodulatory reagent for blocking immunosuppression. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: We examined whether administration of a PD-1 blocking antibody could increase the therapeutic activity of CAR T cells against two different Her-2(+) tumors. The use of a self-antigen mouse model enabled investigation into the efficacy, mechanism, and toxicity of this combination approach. RESULTS: In this study, we first showed a significant increase in the level of PD-1 expressed on transduced anti-Her-2 CD8(+) T cells following antigen-specific stimulation with PD-L1(+) tumor cells and that markers of activation and proliferation were increased in anti-Her-2 T cells in the presence of anti-PD-1 antibody. In adoptive transfer studies in Her-2 transgenic recipient mice, we showed a significant improvement in growth inhibition of two different Her-2(+) tumors treated with anti-Her-2 T cells in combination with anti-PD-1 antibody. The therapeutic effects observed correlated with increased function of anti-Her-2 T cells following PD-1 blockade. Strikingly, a significant decrease in the percentage of Gr1(+) CD11b(+) myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) was observed in the tumor microenvironment of mice treated with the combination therapy. Importantly, increased antitumor effects were not associated with any autoimmune pathology in normal tissue expressing Her-2 antigen. CONCLUSION: This study shows that specifically blocking PD-1 immunosuppression can potently enhance CAR T-cell therapy that has significant implications for potentially improving therapeutic outcomes of this approach in patients with cancer.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo PD-L2 blockade
Flow Cytometry
van der Werf, N., et al (2013). "Th2 cell-intrinsic hypo-responsiveness determines susceptibility to helminth infection" PLoS Pathog 9(3): e1003215.
PubMed
The suppression of protective Type 2 immunity is a principal factor driving the chronicity of helminth infections, and has been attributed to a range of Th2 cell-extrinsic immune-regulators. However, the intrinsic fate of parasite-specific Th2 cells within a chronic immune down-regulatory environment, and the resultant impact such fate changes may have on host resistance is unknown. We used IL-4gfp reporter mice to demonstrate that during chronic helminth infection with the filarial nematode Litomosoides sigmodontis, CD4(+) Th2 cells are conditioned towards an intrinsically hypo-responsive phenotype, characterised by a loss of functional ability to proliferate and produce the cytokines IL-4, IL-5 and IL-2. Th2 cell hypo-responsiveness was a key element determining susceptibility to L. sigmodontis infection, and could be reversed in vivo by blockade of PD-1 resulting in long-term recovery of Th2 cell functional quality and enhanced resistance. Contrasting with T cell dysfunction in Type 1 settings, the control of Th2 cell hypo-responsiveness by PD-1 was mediated through PD-L2, and not PD-L1. Thus, intrinsic changes in Th2 cell quality leading to a functionally hypo-responsive phenotype play a key role in determining susceptibility to filarial infection, and the therapeutic manipulation of Th2 cell-intrinsic quality provides a potential avenue for promoting resistance to helminths.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Holmgaard, R. B., et al (2013). "Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a critical resistance mechanism in antitumor T cell immunotherapy targeting CTLA-4" J Exp Med 210(7): 1389-1402.
PubMed
The cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4)-blocking antibody ipilimumab results in durable responses in metastatic melanoma, though therapeutic benefit has been limited to a fraction of patients. This calls for identification of resistance mechanisms and development of combinatorial strategies. Here, we examine the inhibitory role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) on the antitumor efficacy of CTLA-4 blockade. In IDO knockout mice treated with anti-CTLA-4 antibody, we demonstrate a striking delay in B16 melanoma tumor growth and increased overall survival when compared with wild-type mice. This was also observed with antibodies targeting PD-1-PD-L1 and GITR. To highlight the therapeutic relevance of these findings, we show that CTLA-4 blockade strongly synergizes with IDO inhibitors to mediate rejection of both IDO-expressing and nonexpressing poorly immunogenic tumors, emphasizing the importance of the inhibitory role of both tumor- and host-derived IDO. This effect was T cell dependent, leading to enhanced infiltration of tumor-specific effector T cells and a marked increase in the effector-to-regulatory T cell ratios in the tumors. Overall, these data demonstrate the immunosuppressive role of IDO in the context of immunotherapies targeting immune checkpoints and provide a strong incentive to clinically explore combination therapies using IDO inhibitors irrespective of IDO expression by the tumor cells.
in vivo OX40 activation
in vivo IFNγ neutralization
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Zander, R. A., et al (2015). "PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity" Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641.
PubMed
The differentiation and protective capacity of Plasmodium-specific T cells are regulated by both positive and negative signals during malaria, but the molecular and cellular details remain poorly defined. Here we show that malaria patients and Plasmodium-infected rodents exhibit atypical expression of the co-stimulatory receptor OX40 on CD4 T cells and that therapeutic enhancement of OX40 signaling enhances helper CD4 T cell activity, humoral immunity, and parasite clearance in rodents. However, these beneficial effects of OX40 signaling are abrogated following coordinate blockade of PD-1 co-inhibitory pathways, which are also upregulated during malaria and associated with elevated parasitemia. Co-administration of biologics blocking PD-1 and promoting OX40 signaling induces excessive interferon-gamma that directly limits helper T cell-mediated support of humoral immunity and decreases parasite control. Our results show that targeting OX40 can enhance Plasmodium control and that crosstalk between co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory pathways in pathogen-specific CD4 T cells can impact pathogen clearance.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
in vivo TIM-3 neutralization
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Mittal, D., et al (2014). "Antimetastatic effects of blocking PD-1 and the adenosine A2A receptor" Cancer Res 74(14): 3652-3658.
PubMed
Adenosine targeting is an attractive new approach to cancer treatment, but no clinical study has yet examined adenosine inhibition in oncology despite the safe clinical profile of adenosine A2A receptor inhibitors (A2ARi) in Parkinson disease. Metastasis is the main cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and therefore we have studied experimental and spontaneous mouse models of melanoma and breast cancer metastasis to demonstrate the efficacy and mechanism of a combination of A2ARi in combination with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb). This combination significantly reduces metastatic burden and prolongs the life of mice compared with either monotherapy alone. Importantly, the combination was only effective when the tumor expressed high levels of CD73, suggesting a tumor biomarker that at a minimum could be used to stratify patients that might receive this combination. The mechanism of the combination therapy was critically dependent on NK cells and IFNgamma, and to a lesser extent, CD8(+) T cells and the effector molecule, perforin. Overall, these results provide a strong rationale to use A2ARi with anti-PD-1 mAb for the treatment of minimal residual and metastatic disease.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Triplett, T. A., et al (2018). "Reversal of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated cancer immune suppression by systemic kynurenine depletion with a therapeutic enzyme" Nat Biotechnol 36(8): 758-764.
PubMed
Increased tryptophan (Trp) catabolism in the tumor microenvironment (TME) can mediate immune suppression by upregulation of interferon (IFN)-gamma-inducible indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) and/or ectopic expression of the predominantly liver-restricted enzyme tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO). Whether these effects are due to Trp depletion in the TME or mediated by the accumulation of the IDO1 and/or TDO (hereafter referred to as IDO1/TDO) product kynurenine (Kyn) remains controversial. Here we show that administration of a pharmacologically optimized enzyme (PEGylated kynureninase; hereafter referred to as PEG-KYNase) that degrades Kyn into immunologically inert, nontoxic and readily cleared metabolites inhibits tumor growth. Enzyme treatment was associated with a marked increase in the tumor infiltration and proliferation of polyfunctional CD8(+) lymphocytes. We show that PEG-KYNase administration had substantial therapeutic effects when combined with approved checkpoint inhibitors or with a cancer vaccine for the treatment of large B16-F10 melanoma, 4T1 breast carcinoma or CT26 colon carcinoma tumors. PEG-KYNase mediated prolonged depletion of Kyn in the TME and reversed the modulatory effects of IDO1/TDO upregulation in the TME.
in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Holokai L, Chakrabarti J, Lundy J, Croagh D, Adhikary P, Richards SS, Woodson C, Steele N, Kuester R, Scott A, Khreiss M, Frankel T, Merchant J, Jenkins BJ, Wang J, Shroff RT, Ahmad SA, Zavros Y (2020). "Murine- and Human-Derived Autologous Organoid/
PubMed
Purpose: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has the lowest five-year survival rate of all cancers in the United States. Programmed death 1 receptor (PD-1)-programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) immune checkpoint inhibition has been unsuccessful in clinical trials. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are known to block anti-tumor CD8+ T cell immune responses in various cancers including pancreas. This has led us to our objective that was to develop a clinically relevant in vitro organoid model to specifically target mechanisms that deplete MDSCs as a therapeutic strategy for PDAC. Method: Murine and human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) autologous organoid/immune cell co-cultures were used to test whether PDAC can be effectively treated with combinatorial therapy involving PD-1 inhibition and MDSC depletion. Results: Murine in vivo orthotopic and in vitro organoid/immune cell co-culture models demonstrated that polymorphonuclear (PMN)-MDSCs promoted tumor growth and suppressed cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) proliferation, leading to diminished efficacy of checkpoint inhibition. Mouse- and human-derived organoid/immune cell co-cultures revealed that PD-L1-expressing organoids were unresponsive to nivolumab in vitro in the presence of PMN-MDSCs. Depletion of arginase 1-expressing PMN-MDSCs within these co-cultures rendered the organoids susceptible to anti-PD-1/PD-L1-induced cancer cell death. Conclusions: Here we use mouse- and human-derived autologous pancreatic cancer organoid/immune cell co-cultures to demonstrate that elevated infiltration of polymorphonuclear (PMN)-MDSCs within the PDAC tumor microenvironment inhibit T cell effector function, regardless of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition. We present a pre-clinical model that may predict the efficacy of targeted therapies to improve the outcome of patients with this aggressive and otherwise unpredictable malignancy.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Grasselly, C., et al (2018). "The Antitumor Activity of Combinations of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Is Model-Dependent" Front Immunol 9: 2100.
PubMed
In spite of impressive response rates in multiple cancer types, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are active in only a minority of patients. Alternative strategies currently aim to combine immunotherapies with conventional agents such as cytotoxic chemotherapies. Here, we performed a study of PD-1 or PDL-1 blockade in combination with reference chemotherapies in four fully immunocompetent mouse models of cancer. We analyzed both the in vivo antitumor response, and the tumor immune infiltrate 4 days after the first treatment. in vivo tumor growth experiments revealed variable responsiveness to ICIs between models. We observed enhanced antitumor effects of the combination of immunotherapy with chemotherapy in the MC38 colon and MB49 bladder models, a lack of response in the 4T1 breast model, and an inhibition of ICIs activity in the MBT-2 bladder model. Flow cytometry analysis of tumor samples showed significant differences in all models between untreated and treated mice. At baseline, all the tumor models studied were predominantly infiltrated with cells harboring an immunosuppressive phenotype. Early alterations of the tumor immune infiltrate after treatment were found to be highly variable. We found that the balance between effector cells and immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment could be altered with some treatment combinations, but this effect was not always correlated with an impact on in vivo tumor growth. These results show that the combination of cytotoxic chemotherapy with ICIs may result in enhanced, similar or reduced antitumor activity, in a model- and regimen-dependent fashion. The present investigations should help to select appropriate combination regimens for ICIs.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Triplett, T. A., et al (2018). "Reversal of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated cancer immune suppression by systemic kynurenine depletion with a therapeutic enzyme" Nat Biotechnol 36(8): 758-764.
PubMed
Increased tryptophan (Trp) catabolism in the tumor microenvironment (TME) can mediate immune suppression by upregulation of interferon (IFN)-gamma-inducible indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) and/or ectopic expression of the predominantly liver-restricted enzyme tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO). Whether these effects are due to Trp depletion in the TME or mediated by the accumulation of the IDO1 and/or TDO (hereafter referred to as IDO1/TDO) product kynurenine (Kyn) remains controversial. Here we show that administration of a pharmacologically optimized enzyme (PEGylated kynureninase; hereafter referred to as PEG-KYNase) that degrades Kyn into immunologically inert, nontoxic and readily cleared metabolites inhibits tumor growth. Enzyme treatment was associated with a marked increase in the tumor infiltration and proliferation of polyfunctional CD8(+) lymphocytes. We show that PEG-KYNase administration had substantial therapeutic effects when combined with approved checkpoint inhibitors or with a cancer vaccine for the treatment of large B16-F10 melanoma, 4T1 breast carcinoma or CT26 colon carcinoma tumors. PEG-KYNase mediated prolonged depletion of Kyn in the TME and reversed the modulatory effects of IDO1/TDO upregulation in the TME.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Moynihan, K. D., et al (2016). "Eradication of large established tumors in mice by combination immunotherapy that engages innate and adaptive immune responses" Nat Med. doi : 10.1038/nm.4200.
PubMed
Checkpoint blockade with antibodies specific for cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein (CTLA)-4 or programmed cell death 1 (PDCD1; also known as PD-1) elicits durable tumor regression in metastatic cancer, but these dramatic responses are confined to a minority of patients. This suboptimal outcome is probably due in part to the complex network of immunosuppressive pathways present in advanced tumors, which are unlikely to be overcome by intervention at a single signaling checkpoint. Here we describe a combination immunotherapy that recruits a variety of innate and adaptive immune cells to eliminate large tumor burdens in syngeneic tumor models and a genetically engineered mouse model of melanoma; to our knowledge tumors of this size have not previously been curable by treatments relying on endogenous immunity. Maximal antitumor efficacy required four components: a tumor-antigen-targeting antibody, a recombinant interleukin-2 with an extended half-life, anti-PD-1 and a powerful T cell vaccine. Depletion experiments revealed that CD8+ T cells, cross-presenting dendritic cells and several other innate immune cell subsets were required for tumor regression. Effective treatment induced infiltration of immune cells and production of inflammatory cytokines in the tumor, enhanced antibody-mediated tumor antigen uptake and promoted antigen spreading. These results demonstrate the capacity of an elicited endogenous immune response to destroy large, established tumors and elucidate essential characteristics of combination immunotherapies that are capable of curing a majority of tumors in experimental settings typically viewed as intractable.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Evans, E. E., et al (2015). "Antibody Blockade of Semaphorin 4D Promotes Immune Infiltration into Tumor and Enhances Response to Other Immunomodulatory Therapies" Cancer Immunol Res 3(6): 689-701.
PubMed
Semaphorin 4D (SEMA4D, CD100) and its receptor plexin-B1 (PLXNB1) are broadly expressed in murine and human tumors, and their expression has been shown to correlate with invasive disease in several human tumors. SEMA4D normally functions to regulate the motility and differentiation of multiple cell types, including those of the immune, vascular, and nervous systems. In the setting of cancer, SEMA4D-PLXNB1 interactions have been reported to affect vascular stabilization and transactivation of ERBB2, but effects on immune-cell trafficking in the tumor microenvironment (TME) have not been investigated. We describe a novel immunomodulatory function of SEMA4D, whereby strong expression of SEMA4D at the invasive margins of actively growing tumors influences the infiltration and distribution of leukocytes in the TME. Antibody neutralization of SEMA4D disrupts this gradient of expression, enhances recruitment of activated monocytes and lymphocytes into the tumor, and shifts the balance of cells and cytokines toward a proinflammatory and antitumor milieu within the TME. This orchestrated change in the tumor architecture was associated with durable tumor rejection in murine Colon26 and ERBB2(+) mammary carcinoma models. The immunomodulatory activity of anti-SEMA4D antibody can be enhanced by combination with other immunotherapies, including immune checkpoint inhibition and chemotherapy. Strikingly, the combination of anti-SEMA4D antibody with antibody to CTLA-4 acts synergistically to promote complete tumor rejection and survival. Inhibition of SEMA4D represents a novel mechanism and therapeutic strategy to promote functional immune infiltration into the TME and inhibit tumor progression.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Ngiow, S. F., et al (2015). "A Threshold Level of Intratumor CD8+ T-cell PD1 Expression Dictates Therapeutic Response to Anti-PD1" Cancer Res 75(18): 3800-3811.
PubMed
Despite successes, thus far, a significant proportion of the patients treated with anti-PD1 antibodies have failed to respond. We use mouse tumor models of anti-PD1 sensitivity and resistance and flow cytometry to assess tumor-infiltrating immune cells immediately after therapy. We demonstrate that the expression levels of T-cell PD1 (PD1(lo)), myeloid, and T-cell PDL1 (PDL1(hi)) in the tumor microenvironment inversely correlate and dictate the efficacy of anti-PD1 mAb and function of intratumor CD8(+) T cells. In sensitive tumors, we reveal a threshold for PD1 downregulation on tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T cells below which the release of adaptive immune resistance is achieved. In contrast, PD1(hi) T cells in resistant tumors fail to be rescued by anti-PD1 therapy and remain dysfunctional unless intratumor PDL1(lo) immune cells are targeted. Intratumor Tregs are partly responsible for the development of anti-PD1-resistant tumors and PD1(hi) CD8(+) T cells. Our analyses provide a framework to interrogate intratumor CD8(+) T-cell PD1 and immune PDL1 levels and response in human cancer. Cancer Res; 75(18); 3800-11. (c)2015 AACR.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Twyman-Saint Victor, C., et al (2015). "Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer" Nature 520(7547): 373-377.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors result in impressive clinical responses, but optimal results will require combination with each other and other therapies. This raises fundamental questions about mechanisms of non-redundancy and resistance. Here we report major tumour regressions in a subset of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with an anti-CTLA4 antibody (anti-CTLA4) and radiation, and reproduced this effect in mouse models. Although combined treatment improved responses in irradiated and unirradiated tumours, resistance was common. Unbiased analyses of mice revealed that resistance was due to upregulation of PD-L1 on melanoma cells and associated with T-cell exhaustion. Accordingly, optimal response in melanoma and other cancer types requires radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1/PD-1. Anti-CTLA4 predominantly inhibits T-regulatory cells (Treg cells), thereby increasing the CD8 T-cell to Treg (CD8/Treg) ratio. Radiation enhances the diversity of the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire of intratumoral T cells. Together, anti-CTLA4 promotes expansion of T cells, while radiation shapes the TCR repertoire of the expanded peripheral clones. Addition of PD-L1 blockade reverses T-cell exhaustion to mitigate depression in the CD8/Treg ratio and further encourages oligoclonal T-cell expansion. Similarly to results from mice, patients on our clinical trial with melanoma showing high PD-L1 did not respond to radiation plus anti-CTLA4, demonstrated persistent T-cell exhaustion, and rapidly progressed. Thus, PD-L1 on melanoma cells allows tumours to escape anti-CTLA4-based therapy, and the combination of radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1 promotes response and immunity through distinct mechanisms.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Vanpouille-Box, C., et al (2015). "TGFbeta Is a Master Regulator of Radiation Therapy-Induced Antitumor Immunity" Cancer Res 75(11): 2232-2242.
PubMed
T cells directed to endogenous tumor antigens are powerful mediators of tumor regression. Recent immunotherapy advances have identified effective interventions to unleash tumor-specific T-cell activity in patients who naturally develop them. Eliciting T-cell responses to a patient’s individual tumor remains a major challenge. Radiation therapy can induce immune responses to model antigens expressed by tumors, but it remains unclear whether it can effectively prime T cells specific for endogenous antigens expressed by poorly immunogenic tumors. We hypothesized that TGFbeta activity is a major obstacle hindering the ability of radiation to generate an in situ tumor vaccine. Here, we show that antibody-mediated TGFbeta neutralization during radiation therapy effectively generates CD8(+) T-cell responses to multiple endogenous tumor antigens in poorly immunogenic mouse carcinomas. Generated T cells were effective at causing regression of irradiated tumors and nonirradiated lung metastases or synchronous tumors (abscopal effect). Gene signatures associated with IFNgamma and immune-mediated rejection were detected in tumors treated with radiation therapy and TGFbeta blockade in combination but not as single agents. Upregulation of programmed death (PD) ligand-1 and -2 in neoplastic and myeloid cells and PD-1 on intratumoral T cells limited tumor rejection, resulting in rapid recurrence. Addition of anti-PD-1 antibodies extended survival achieved with radiation and TGFbeta blockade. Thus, TGFbeta is a fundamental regulator of radiation therapy’s ability to generate an in situ tumor vaccine. The combination of local radiation therapy with TGFbeta neutralization offers a novel individualized strategy for vaccinating patients against their tumors.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Zander, R. A., et al (2015). "PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity" Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641.
PubMed
The differentiation and protective capacity of Plasmodium-specific T cells are regulated by both positive and negative signals during malaria, but the molecular and cellular details remain poorly defined. Here we show that malaria patients and Plasmodium-infected rodents exhibit atypical expression of the co-stimulatory receptor OX40 on CD4 T cells and that therapeutic enhancement of OX40 signaling enhances helper CD4 T cell activity, humoral immunity, and parasite clearance in rodents. However, these beneficial effects of OX40 signaling are abrogated following coordinate blockade of PD-1 co-inhibitory pathways, which are also upregulated during malaria and associated with elevated parasitemia. Co-administration of biologics blocking PD-1 and promoting OX40 signaling induces excessive interferon-gamma that directly limits helper T cell-mediated support of humoral immunity and decreases parasite control. Our results show that targeting OX40 can enhance Plasmodium control and that crosstalk between co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory pathways in pathogen-specific CD4 T cells can impact pathogen clearance.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Zelenay, S., et al (2015). "Cyclooxygenase-Dependent Tumor Growth through Evasion of Immunity" Cell 162(6): 1257-1270.
PubMed
The mechanisms by which melanoma and other cancer cells evade anti-tumor immunity remain incompletely understood. Here, we show that the growth of tumors formed by mutant Braf(V600E) mouse melanoma cells in an immunocompetent host requires their production of prostaglandin E2, which suppresses immunity and fuels tumor-promoting inflammation. Genetic ablation of cyclooxygenases (COX) or prostaglandin E synthases in Braf(V600E) mouse melanoma cells, as well as in Nras(G12D) melanoma or in breast or colorectal cancer cells, renders them susceptible to immune control and provokes a shift in the tumor inflammatory profile toward classic anti-cancer immune pathways. This mouse COX-dependent inflammatory signature is remarkably conserved in human cutaneous melanoma biopsies, arguing for COX activity as a driver of immune suppression across species. Pre-clinical data demonstrate that inhibition of COX synergizes with anti-PD-1 blockade in inducing eradication of tumors, implying that COX inhibitors could be useful adjuvants for immune-based therapies in cancer patients.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
McGray, A. J., et al (2014). "Immunotherapy-induced CD8+ T cells instigate immune suppression in the tumor" Mol Ther 22(1): 206-218.
PubMed
Despite clear evidence of immunogenicity, cancer vaccines only provide a modest clinical benefit. To evaluate the mechanisms that limit tumor regression following vaccination, we have investigated the weak efficacy of a highly immunogenic experimental vaccine using a murine melanoma model. We discovered that the tumor adapts rapidly to the immune attack instigated by tumor-specific CD8+ T cells in the first few days following vaccination, resulting in the upregulation of a complex set of biological networks, including multiple immunosuppressive processes. This rapid adaptation acts to prevent sustained local immune attack, despite continued infiltration by increasing numbers of tumor-specific T cells. Combining vaccination with adoptive transfer of tumor-specific T cells produced complete regression of the treated tumors but did not prevent the adaptive immunosuppression. In fact, the adaptive immunosuppressive pathways were more highly induced in regressing tumors, commensurate with the enhanced level of immune attack. Examination of tumor infiltrating T-cell functionality revealed that the adaptive immunosuppression leads to a progressive loss in T-cell function, even in tumors that are regressing. These novel observations that T cells produced by therapeutic intervention can instigate a rapid adaptive immunosuppressive response within the tumor have important implications for clinical implementation of immunotherapies.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Mittal, D., et al (2014). "Antimetastatic effects of blocking PD-1 and the adenosine A2A receptor" Cancer Res 74(14): 3652-3658.
PubMed
Adenosine targeting is an attractive new approach to cancer treatment, but no clinical study has yet examined adenosine inhibition in oncology despite the safe clinical profile of adenosine A2A receptor inhibitors (A2ARi) in Parkinson disease. Metastasis is the main cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and therefore we have studied experimental and spontaneous mouse models of melanoma and breast cancer metastasis to demonstrate the efficacy and mechanism of a combination of A2ARi in combination with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb). This combination significantly reduces metastatic burden and prolongs the life of mice compared with either monotherapy alone. Importantly, the combination was only effective when the tumor expressed high levels of CD73, suggesting a tumor biomarker that at a minimum could be used to stratify patients that might receive this combination. The mechanism of the combination therapy was critically dependent on NK cells and IFNgamma, and to a lesser extent, CD8(+) T cells and the effector molecule, perforin. Overall, these results provide a strong rationale to use A2ARi with anti-PD-1 mAb for the treatment of minimal residual and metastatic disease.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
John, L. B., et al (2013). "Anti-PD-1 antibody therapy potently enhances the eradication of established tumors by gene-modified T cells" Clin Cancer Res 19(20): 5636-5646.
PubMed
PURPOSE: To determine the antitumor efficacy and toxicity of a novel combination approach involving adoptive T-cell immunotherapy using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells with an immunomodulatory reagent for blocking immunosuppression. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: We examined whether administration of a PD-1 blocking antibody could increase the therapeutic activity of CAR T cells against two different Her-2(+) tumors. The use of a self-antigen mouse model enabled investigation into the efficacy, mechanism, and toxicity of this combination approach. RESULTS: In this study, we first showed a significant increase in the level of PD-1 expressed on transduced anti-Her-2 CD8(+) T cells following antigen-specific stimulation with PD-L1(+) tumor cells and that markers of activation and proliferation were increased in anti-Her-2 T cells in the presence of anti-PD-1 antibody. In adoptive transfer studies in Her-2 transgenic recipient mice, we showed a significant improvement in growth inhibition of two different Her-2(+) tumors treated with anti-Her-2 T cells in combination with anti-PD-1 antibody. The therapeutic effects observed correlated with increased function of anti-Her-2 T cells following PD-1 blockade. Strikingly, a significant decrease in the percentage of Gr1(+) CD11b(+) myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) was observed in the tumor microenvironment of mice treated with the combination therapy. Importantly, increased antitumor effects were not associated with any autoimmune pathology in normal tissue expressing Her-2 antigen. CONCLUSION: This study shows that specifically blocking PD-1 immunosuppression can potently enhance CAR T-cell therapy that has significant implications for potentially improving therapeutic outcomes of this approach in patients with cancer.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
van der Werf, N., et al (2013). "Th2 cell-intrinsic hypo-responsiveness determines susceptibility to helminth infection" PLoS Pathog 9(3): e1003215.
PubMed
The suppression of protective Type 2 immunity is a principal factor driving the chronicity of helminth infections, and has been attributed to a range of Th2 cell-extrinsic immune-regulators. However, the intrinsic fate of parasite-specific Th2 cells within a chronic immune down-regulatory environment, and the resultant impact such fate changes may have on host resistance is unknown. We used IL-4gfp reporter mice to demonstrate that during chronic helminth infection with the filarial nematode Litomosoides sigmodontis, CD4(+) Th2 cells are conditioned towards an intrinsically hypo-responsive phenotype, characterised by a loss of functional ability to proliferate and produce the cytokines IL-4, IL-5 and IL-2. Th2 cell hypo-responsiveness was a key element determining susceptibility to L. sigmodontis infection, and could be reversed in vivo by blockade of PD-1 resulting in long-term recovery of Th2 cell functional quality and enhanced resistance. Contrasting with T cell dysfunction in Type 1 settings, the control of Th2 cell hypo-responsiveness by PD-1 was mediated through PD-L2, and not PD-L1. Thus, intrinsic changes in Th2 cell quality leading to a functionally hypo-responsive phenotype play a key role in determining susceptibility to filarial infection, and the therapeutic manipulation of Th2 cell-intrinsic quality provides a potential avenue for promoting resistance to helminths.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Holmgaard, R. B., et al (2013). "Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a critical resistance mechanism in antitumor T cell immunotherapy targeting CTLA-4" J Exp Med 210(7): 1389-1402.
PubMed
The cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4)-blocking antibody ipilimumab results in durable responses in metastatic melanoma, though therapeutic benefit has been limited to a fraction of patients. This calls for identification of resistance mechanisms and development of combinatorial strategies. Here, we examine the inhibitory role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) on the antitumor efficacy of CTLA-4 blockade. In IDO knockout mice treated with anti-CTLA-4 antibody, we demonstrate a striking delay in B16 melanoma tumor growth and increased overall survival when compared with wild-type mice. This was also observed with antibodies targeting PD-1-PD-L1 and GITR. To highlight the therapeutic relevance of these findings, we show that CTLA-4 blockade strongly synergizes with IDO inhibitors to mediate rejection of both IDO-expressing and nonexpressing poorly immunogenic tumors, emphasizing the importance of the inhibitory role of both tumor- and host-derived IDO. This effect was T cell dependent, leading to enhanced infiltration of tumor-specific effector T cells and a marked increase in the effector-to-regulatory T cell ratios in the tumors. Overall, these data demonstrate the immunosuppressive role of IDO in the context of immunotherapies targeting immune checkpoints and provide a strong incentive to clinically explore combination therapies using IDO inhibitors irrespective of IDO expression by the tumor cells.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Curran, M. A., et al (2010). "PD-1 and CTLA-4 combination blockade expands infiltrating T cells and reduces regulatory T and myeloid cells within B16 melanoma tumors" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(9): 4275-4280.
PubMed
Vaccination with irradiated B16 melanoma cells expressing either GM-CSF (Gvax) or Flt3-ligand (Fvax) combined with antibody blockade of the negative T-cell costimulatory receptor cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) promotes rejection of preimplanted tumors. Despite CTLA-4 blockade, T-cell proliferation and cytokine production can be inhibited by the interaction of programmed death-1 (PD-1) with its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 or by the interaction of PD-L1 with B7-1. Here, we show that the combination of CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade is more than twice as effective as either alone in promoting the rejection of B16 melanomas in conjunction with Fvax. Adding alphaPD-L1 to this regimen results in rejection of 65% of preimplanted tumors vs. 10% with CTLA-4 blockade alone. Combination PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade increases effector T-cell (Teff) infiltration, resulting in highly advantageous Teff-to-regulatory T-cell ratios with the tumor. The fraction of tumor-infiltrating Teffs expressing CTLA-4 and PD-1 increases, reflecting the proliferation and accumulation of cells that would otherwise be anergized. Combination blockade also synergistically increases Teff-to-myeloid-derived suppressor cell ratios within B16 melanomas. IFN-gamma production increases in both the tumor and vaccine draining lymph nodes, as does the frequency of IFN-gamma/TNF-alpha double-producing CD8(+) T cells within the tumor. These results suggest that combination blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1- and CTLA-4-negative costimulatory pathways allows tumor-specific T cells that would otherwise be inactivated to continue to expand and carry out effector functions, thereby shifting the tumor microenvironment from suppressive to inflammatory.
Product Citations
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Neuroscience
-
Cancer Research
Conditionally replicative adenovirus as a therapy for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.
In Molecular Therapy. Oncology on 20 June 2024 by Nikrad, J. A., Galvin, R. T., et al.
Oncolytic adenoviruses (Ads) stand out as a promising strategy for the targeted infection and lysis of tumor cells, with well-established clinical utility across various malignancies. This study delves into the therapeutic potential of oncolytic Ads in the context of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs). Specifically, we evaluate conditionally replicative adenoviruses (CRAds) driven by the cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) promoter, as selective agents against MPNSTs, demonstrating their preferential targeting of MPNST cells compared with non-malignant Schwann cell control. COX2-driven CRAds, particularly those with modified fiber-knobs exhibit superior binding affinity toward MPNST cells and demonstrate efficient and preferential replication and lysis of MPNST cells, with minimal impact on non-malignant control cells. In vivo experiments involving intratumoral CRAd injections in immunocompromised mice with human MPNST xenografts significantly extend survival and reduce tumor growth rate compared with controls. Moreover, in immunocompetent mouse models with MPNST-like allografts, CRAd injections induce a robust infiltration of CD8+ T cells into the tumor microenvironment (TME), indicating the potential to promote a pro-inflammatory response. These findings underscore oncolytic Ads as promising, selective, and minimally toxic agents for MPNST therapy, warranting further exploration.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Inhibiting PLA2G7 reverses the immunosuppressive function of intratumoral macrophages and augments immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 25 January 2024 by Zhang, F., Liu, W., et al.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an exceptionally immunosuppressive malignancy characterized by limited treatment options and a dismal prognosis. Macrophages constitute the primary and heterogeneous immune cell population within the HCC microenvironment. Our objective is to identify distinct subsets of macrophages implicated in the progression of HCC and their resistance to immunotherapy. Intratumoral macrophage-specific marker genes were identified via single-cell RNA sequencing analyses. The clinical relevance of phospholipase A2 Group VII (PLA2G7), a pivotal enzyme in phospholipid metabolism, was assessed in patients with HCC through immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Flow cytometry and an in vitro co-culture system were used to elucidate the specific role of PLA2G7 in macrophages. Orthotopic and subcutaneous HCC mouse models were employed to evaluate the potential of the PLA2G7 inhibitor in complementing immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. Single-cell RNA sequencing analyses disclosed predominant PLA2G7 expression in intratumoral macrophages within the HCC microenvironment. The macrophage-specific PLA2G7 was significantly correlated with poorer prognosis and immunotherapy resistance in patients with HCC. PLA2G7high macrophages represent a highly immunosuppressive subset and impede CD8 T-cell activation. Pharmacological inhibition of PLA2G7 by darapladib improved the therapeutic efficacy of anti-programmed cell death protein 1 antibodies in the HCC mouse models. Macrophage-specific PLA2G7 serves as a novel biomarker capable of prognosticating immunotherapy responsiveness and inhibiting PLA2G7 has the potential to enhance the efficacy of ICB therapy for HCC. © Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
HDAC6 inhibitor ACY-1215 enhances STAT1 acetylation to block PD-L1 for colorectal cancer immunotherapy.
In Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy : CII on 17 January 2024 by Wen, Y., Ye, S., et al.
The search for effective combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) has become important for cancer patients who do not respond to the ICI well. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors have attracted wide attention as anti-tumor agents. ACY-1215 is a selective inhibitor of HDAC6, which can inhibit the growth of a variety of tumor. We previously revealed that HDAC family is highly expressed in colorectal cancer specimens and mouse models. In this study, ACY-1215 was combined with anti-PD1 to treat tumor-bearing mice associated with colorectal cancer. ACY-1215 combined with anti-PD1 effectively inhibited the colorectal tumor growth. The expression of PD-L1 in tumor of mice were inhibited by ACY-1215 and anti-PD1 combination treatment, whereas some biomarkers reflecting T cell activation were upregulated. In a co-culture system of T cells and tumor cells, ACY-1215 helped T cells to kill tumor cells. Mechanically, HDAC6 enhanced the acetylation of STAT1 and inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT1, thus preventing STAT1 from entering the nucleus to activate PD-L1 transcription. This study reveals a novel regulatory mechanism of HDAC6 on non-histone substrates, especially on protein acetylation. HDAC6 inhibitors may be of great significance in tumor immunotherapy and related combination strategies. © 2024. The Author(s).
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Genetics
-
Cancer Research
Dual role of CD73 as a signaling molecule and adenosine-generating enzyme in colorectal cancer progression and immune evasion.
In International Journal of Biological Sciences on 2 January 2024 by Lian, W., Jiang, D., et al.
Metastasis and limited benefits of immune checkpoint blockade are two obstacles to the battle against colorectal cancer (CRC). CD73, encoded by the gene 5'-Nucleotidase Ecto (NT5E), is a major enzyme that generates extracellular adenosine. However, whether CD73 affects cancer progression and immune response in CRC remains unclear. Here, the clinical significance of CD73 was assessed in human CRC specimens using immunohistochemistry and bioinformatic analyses. We demonstrated that CD73 is elevated in CRC tissues, particularly in those with metastasis, and correlates with poor prognosis. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments demonstrate that tumor CD73 supports tumor progression and impairs the viability and effector functions of CD8+ T cells. Targeting CD73 on CRC cells reduces their malignant phenotypes and improves the anti-cancer response of CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Moreover, the combination of CD73 blockade and PD-1 inhibitors exhibited enhanced anti-cancer effects when compared to a single-agent treatment. Thus, CD73 may be a promising target in the treatment of CRC. © The author(s).
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
XTX101, a tumor-activated, Fc-enhanced anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody, demonstrates tumor-growth inhibition and tumor-selective pharmacodynamics in mouse models of cancer.
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 12 December 2023 by Jenkins, K. A., Park, M., et al.
The clinical benefit of the anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody (mAb) ipilimumab has been well established but limited by immune-related adverse events, especially when ipilimumab is used in combination with anti-PD-(L)1 mAb therapy. To overcome these limitations, we have developed XTX101, a tumor-activated, Fc-enhanced anti-CTLA-4 mAb. XTX101 consists of an anti-human CTLA-4 mAb covalently linked to masking peptides that block the complementarity-determining regions, thereby minimizing the mAb binding to CTLA-4. The masking peptides are designed to be released by proteases that are typically dysregulated within the tumor microenvironment (TME), resulting in activation of XTX101 intratumorally. Mutations within the Fc region of XTX101 were included to enhance affinity for FcγRIII, which is expected to enhance potency through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Biophysical, biochemical, and cell-based assays demonstrate that the function of XTX101 depends on proteolytic activation. In human CTLA-4 transgenic mice, XTX101 monotherapy demonstrated significant tumor growth inhibition (TGI) including complete responses, increased intratumoral CD8+T cells, and regulatory T cell depletion within the TME while maintaining minimal pharmacodynamic effects in the periphery. XTX101 in combination with anti-PD-1 mAb treatment resulted in significant TGI and was well tolerated in mice. XTX101 was activated in primary human tumors across a range of tumor types including melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, colon cancer and lung cancer in an ex vivo assay system. These data demonstrate that XTX101 retains the full potency of an Fc-enhanced CTLA-4 antagonist within the TME while minimizing the activity in non-tumor tissue, supporting the further evaluation of XTX101 in clinical studies. © Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Secreted antigen A peptidoglycan hydrolase is essential forEnterococcus faeciumcell separation and priming of immune checkpoint inhibitor cancer therapy
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 19 November 2023 by Klupt, S., Fam, K. T., et al.
Introductory paragraph Enterococcus faecium is a microbiota species in humans that can modulate host immunity 1 , but has also acquired antibiotic resistance and is a major cause of hospital-associated infections 2 . Notably, diverse strains of E. faecium produce SagA, a highly conserved peptidoglycan hydrolase that is sufficient to promote intestinal immunity 3–5 and immune checkpoint inhibitor antitumor activity 6 . However, the essential functions of SagA in E. faecium were unknown. Here we report that deletion of sagA impaired E. faecium growth and resulted in bulged and clustered enterococci due to defective peptidoglycan cleavage and cell separation. Moreover, Δ sagA showed increased antibiotic sensitivity, yielded lower levels of active muropeptides, displayed reduced activation of the peptidoglycan pattern-recognition receptor NOD2, and failed to promote cancer immunotherapy. Importantly, plasmid-based expression of SagA, but not its catalytically-inactive mutant, restored Δ sagA growth, production of active muropeptides and NOD2 activation. SagA is therefore essential for E. faecium growth, stress resistance and activation of host immunity.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Roseburia intestinalis generated butyrate boosts anti-PD-1 efficacy in colorectal cancer by activating cytotoxic CD8+ T cells.
In Gut on 1 November 2023 by Kang, X., Liu, C., et al.
Roseburia intestinalis is a probiotic species that can suppress intestinal inflammation by producing metabolites. We aimed to study the role of R. intestinalis in colorectal tumourigenesis and immunotherapy. R. intestinalis abundance was evaluated in stools of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) (n=444) and healthy controls (n=575). The effects of R. intestinalis were studied in ApcMin/+ or azoxymethane (AOM)-induced CRC mouse models, and in syngeneic mouse xenograft models of CT26 (microsatellite instability (MSI)-low) or MC38 (MSI-high). The change of immune landscape was evaluated by multicolour flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry staining. Metabolites were profiled by metabolomic profiling. R. intestinalis was significantly depleted in stools of patients with CRC compared with healthy controls. R. intestinalis administration significantly inhibited tumour formation in ApcMin/+ mice, which was confirmed in mice with AOM-induced CRC. R. intestinalis restored gut barrier function as indicated by improved intestinal permeability and enhanced expression of tight junction proteins. Butyrate was identified as the functional metabolite generated by R. intestinalis. R. intestinalis or butyrate suppressed tumour growth by inducing cytotoxic granzyme B+, interferon (IFN)-γ+ and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α+ CD8+ T cells in orthotopic mouse models of MC38 or CT26. R. intestinalis or butyrate also significantly improved antiprogrammed cell death protein 1 (anti-PD-1) efficacy in mice bearing MSI-low CT26 tumours. Mechanistically, butyrate directly bound to toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) receptor on CD8+ T cells to induce its activity through activating nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signalling. R. intestinalis protects against colorectal tumourigenesis by producing butyrate, which could also improve anti-PD-1 efficacy by inducing functional CD8+ T cells. R. intestinalis is a potential adjuvant to augment anti-PD-1 efficacy against CRC. © Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Angiopoietin-2 blockade suppresses growth of liver metastases from pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors by promoting T cell recruitment.
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 16 October 2023 by Lee, E., O'Keefe, S., et al.
Improving the management of metastasis in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs) is critical, as nearly half of patients with PanNETs present with liver metastases, and this accounts for the majority of patient mortality. We identified angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) as one of the most upregulated angiogenic factors in RNA-Seq data from human PanNET liver metastases and found that higher ANGPT2 expression correlated with poor survival rates. Immunohistochemical staining revealed that ANGPT2 was localized to the endothelial cells of blood vessels in PanNET liver metastases. We observed an association between the upregulation of endothelial ANGPT2 and liver metastatic progression in both patients and transgenic mouse models of PanNETs. In human and mouse PanNET liver metastases, ANGPT2 upregulation coincided with poor T cell infiltration, indicative of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Notably, both pharmacologic inhibition and genetic deletion of ANGPT2 in PanNET mouse models slowed the growth of PanNET liver metastases. Furthermore, pharmacologic inhibition of ANGPT2 promoted T cell infiltration and activation in liver metastases, improving the survival of mice with metastatic PanNETs. These changes were accompanied by reduced plasma leakage and improved vascular integrity in metastases. Together, these findings suggest that ANGPT2 blockade may be an effective strategy for promoting T cell infiltration and immunostimulatory reprogramming to reduce the growth of liver metastases in PanNETs.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
Intratumoral Administration of High-Concentration Nitric Oxide and Anti-mPD-1 Treatment Improves Tumor Regression Rates and Survival in CT26 Tumor-Bearing Mice.
In Cells on 11 October 2023 by Confino, H., Sela, Y., et al.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have transformed clinical oncology. However, their use is limited as response is observed in only ~20-50% of patients. Previously, we demonstrated that treating CT26 tumor-bearing mice with ultra-high-concentration gaseous nitric oxide (UNO) followed by tumor resection stimulated antitumor immune responses. Accordingly, UNO may improve tumor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Here, we investigated the ability of UNO to improve the efficacy of a programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) antibody in vitro and in treating CT26 tumor-bearing mice. CT26 cells were injected into the flank of Balb/c mice (n = 15-16 per group). On day 6, CT26 cells were injected into the contralateral flank, and anti-mPD-1 injections commenced. Primary tumors were treated with intratumoral UNO on day 8. Tumor volume, response rates, toxicity, and survival were monitored. (1) Short exposure to 25,000-100,000 parts per million (ppm) UNO in vitro resulted in significant upregulation of PD-L1 expression on CT26 cells. (2) UNO treatment in vivo consistently reduced cell viability in CT26 tumors. (3) Treatment reduced regulatory T-cell (Treg) levels in the tumor and increased levels of systemic M1 macrophages. UNO responders had increased CD8+ T-cell tumor infiltration. (4) Nine days after treatment, primary tumor growth was significantly lower in the combination arm vs. anti-mPD-1 alone (p = 0.0005). (5) Complete tumor regression occurred in 8/15 (53%) of mice treated with a combination of 10 min UNO and anti-mPD-1, 100 days post-treatment, compared to 4/16 (25%) of controls treated with anti-mPD-1 alone (p = 0.1489). (6) There was no toxicity associated with UNO treatment. (7) Combination treatment showed a trend toward increased survival 100 days post-treatment compared to anti-mPD-1 alone (p = 0.0653). Combining high-concentration NO and immune checkpoint inhibitors warrants further assessment especially in tumors resistant to checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
BATF relieves hepatic steatosis by inhibiting PD1 and promoting energy metabolism.
In eLife on 15 September 2023 by Zhang, Z., Liao, Q., et al.
The rising prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a global health threat that needs to be addressed urgently. Basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor (BATF) is commonly thought to be involved in immunity, but its effect on lipid metabolism is not clear. Here, we investigated the function of BATF in hepatic lipid metabolism. BATF alleviated high-fat diet (HFD)-induced hepatic steatosis and inhibited elevated programmed cell death protein (PD)1 expression induced by HFD. A mechanistic study confirmed that BATF regulated fat accumulation by inhibiting PD1 expression and promoting energy metabolism. PD1 antibodies alleviated hepatic lipid deposition. In conclusion, we identified the regulatory role of BATF in hepatic lipid metabolism and that PD1 is a target for alleviation of NAFLD. This study provides new insights into the relationship between BATF, PD1, and NAFLD. © 2023, Zhang, Liao et al.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Orchestrating antigen delivery and presentation efficiency in lymph node by nanoparticle shape for immune response.
In Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. B on 1 September 2023 by Zhao, H., Li, Y., et al.
Activating humoral and cellular immunity in lymph nodes (LNs) of nanoparticle-based vaccines is critical to controlling tumors. However, how the physical properties of nanovaccine carriers orchestrate antigen capture, lymphatic delivery, antigen presentation and immune response in LNs is largely unclear. Here, we manufactured gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with the same size but different shapes (cages, rods, and stars), and loaded tumor antigen as nanovaccines to explore their disparate characters on above four areas. Results revealed that star-shaped AuNPs captured and retained more repetitive antigen epitopes. On lymphatic delivery, both rods and star-shaped nanovaccines mainly drain into the LN follicles region while cage-shaped showed stronger paracortex retention. A surprising finding is that the star-shaped nanovaccines elicited potent humoral immunity, which is mediated by CD4+ T helper cell and follicle B cell cooperation significantly preventing tumor growth in the prophylactic study. Interestingly, cage-shaped nanovaccines preferentially presented peptide-MHC I complexes to evoke robust CD8+ T cell immunity and showed the strongest therapeutic efficacy when combined with the PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor in established tumor study. These results highlight the importance of nanoparticle shape on antigen delivery and presentation for immune response in LNs, and our findings support the notion that different design strategies are required for prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines. © 2023 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Hsp70-Targeting and Size-Tunable Nanoparticles Combine with PD-1 Checkpoint Blockade to Treat Glioma.
In Small (Weinheim An Der Bergstrasse, Germany) on 1 September 2023 by Xie, R., Wang, Y., et al.
Invasive glioma usually disrupts the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), making the delivery of nanodrugs across the BBB possible, but sufficient targeting ability is still avidly needed to improve drug accumulation in glioma. Membrane-bound heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) is expressed on the membrane of glioma cells rather than adjacent normal cells, therefore it can serve as a specific glioma target. Meanwhile, prolonging the retention in tumors is important for active-targeting nanoparticles to overcome receptor-binding barriers. Herein, the Hsp70-targeting and acid-triggered self-assembled gold nanoparticles (D-A-DA/TPP) are proposed to realize selective delivery of doxorubicin (DOX) to glioma. In the weakly acidic glioma matrix, D-A-DA/TPP formed aggregates to prolong retention, improve receptor-binding efficiency and facilitate acid-responsive DOX release. DOX accumulation in glioma induced immunogenic cell death (ICD) to promote antigen presentation. Meanwhile, combination with the PD-1 checkpoint blockade further activate T cells and provokes robust anti-tumor immunity. The results showed that D-A-DA/TPP can induce more glioma apoptosis. Furthermore, in vivo studies indicated D-A-DA/TPP plus PD-1 checkpoint blockade significantly improved median survival time. This study offeres a potential nanocarrier combining size-tunable strategy with active targeting ability to increase drug enrichment in glioma and synergizes with PD-1 checkpoint blockade to achieve chemo-immunotherapy. © 2023 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Biosynthesized gold nanoparticles that activate Toll-like receptors and elicit localized light-converting hyperthermia for pleiotropic tumor immunoregulation.
In Nature Communications on 24 August 2023 by Qin, H., Chen, Y., et al.
Manipulating the tumor immune contexture towards a more active state can result in better therapeutic outcomes. Here we describe an easily accessible bacterial biomineralization-generated immunomodulator, which we name Ausome (Au + [exo]some). Ausome comprises a gold nanoparticle core covered by bacterial components; the former affords an inducible hyperthermia effect, while the latter mobilizes diverse immune responses. Multiple pattern recognition receptors actively participate in Ausome-initiated immune responses, which lead to the release of a broad spectrum of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the activation of effector immune cells. Upon laser irradiation, tumor-accumulated Ausome elicits a hyperthermic response, which improves tissue blood perfusion and contributes to enhanced infiltration of immunostimulatory modules, including cytokines and effector lymphocytes. This immune-modulating strategy mediated by Ausome ultimately brings about a comprehensive immune reaction and selectively amplifies the effects of local antitumor immunity, enhancing the efficacy of well-established chemo- or immuno-therapies in preclinical cancer models in female mice. © 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals enhanced antitumor immunity after combined application of PD-1 inhibitor and Shenmai injection in non-small cell lung cancer.
In Cell Communication and Signaling : CCS on 10 July 2023 by Yu, D., Yang, P., et al.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have altered the clinical management of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the low response rate, severe immune-related adverse events (irAEs), and hyperprogressive disease following ICIs monotherapy require attention. Combination therapy may overcome these limitations and traditional Chinese medicine with immunomodulatory effects provides a promising approach. Shenmai injection (SMI) is a clinically effective adjuvant treatment for cancer with chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Therefore, the combined effects and mechanisms of SMI and programmed death-1 (PD-1) inhibitor against NSCLC was focused on this study. A Lewis lung carcinoma mouse model and a lung squamous cell carcinoma humanized mouse model were used to investigate the combined efficacy and safety of SMI and PD-1 inhibitor. The synergistic mechanisms of the combination therapy against NSCLC were explored using single-cell RNA sequencing. Validation experiments were performed using immunofluorescence analysis, in vitro experiment, and bulk transcriptomic datasets. In both models, combination therapy alleviated tumor growth and prolonged survival without increasing irAEs. The GZMAhigh and XCL1high natural killer (NK) cell subclusters with cytotoxic and chemokine signatures increased in the combination therapy, while malignant cells from combination therapy were mainly in the apoptotic state, suggesting that mediating tumor cell apoptosis through NK cells is the main synergistic mechanisms of combination therapy. In vitro experiment confirmed that combination therapy increased secretion of Granzyme A by NK cells. Moreover, we discovered that PD-1 inhibitor and SMI combination blocked inhibitory receptors on NK and T cells and restores their antitumoral activity in NSCLC better than PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy, and immune and stromal cells exhibited a decrease of angiogenic features and attenuated cancer metabolism reprogramming in microenvironment of combination therapy. This study demonstrated that SMI reprograms tumor immune microenvironment mainly by inducing NK cells infiltration and synergizes with PD-1 inhibitor against NSCLC, suggested that targeting NK cells may be an important strategy for combining with ICIs. Video Abstract. © 2023. The Author(s).
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Immune checkpoint activity regulates polycystic kidney disease progression.
In JCI Insight on 22 June 2023 by Kleczko, E. K., Nguyen, D. T., et al.
Innate and adaptive immune cells modulate the severity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), a common kidney disease with inadequate treatment options. ADPKD has parallels with cancer, in which immune checkpoint inhibitors have been shown to reactivate CD8+ T cells and slow tumor growth. We have previously shown that in PKD, CD8+ T cell loss worsens disease. This study used orthologous early-onset and adult-onset ADPKD models (Pkd1 p.R3277C) to evaluate the role of immune checkpoints in PKD. Flow cytometry of kidney cells showed increased levels of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) on T cells and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1)/CD80 on macrophages and epithelial cells in Pkd1RC/RC mice versus WT, paralleling disease severity. PD-L1/CD80 was also upregulated in ADPKD human cells and patient kidney tissue versus controls. Genetic PD-L1 loss or treatment with an anti-PD-1 antibody did not impact PKD severity in early-onset or adult-onset ADPKD models. However, treatment with anti-PD-1 plus anti-CTLA-4, blocking 2 immune checkpoints, improved PKD outcomes in adult-onset ADPKD mice; neither monotherapy altered PKD severity. Combination therapy resulted in increased kidney CD8+ T cell numbers/activation and decreased kidney regulatory T cell numbers correlative with PKD severity. Together, our data suggest that immune checkpoint activation is an important feature of and potential novel therapeutic target in ADPKD.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
EZH2 inhibition promotes tumor immunogenicity in lung squamous cell carcinomas
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 8 June 2023 by DuCote, T. J., Song, X., et al.
ABSTRACT Two important factors that contribute to resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are an immune-suppressive microenvironment and limited antigen presentation by tumor cells. In this study, we examine if inhibition of the methyltransferase EZH2 can increase ICI response in lung squamous cell carcinomas (LSCCs). Our in vitro experiments using 2D human cancer cell lines as well as 3D murine and patient derived organoids treated with two inhibitors of the EZH2 plus interferon-γ (IFNγ) showed that EZH2 inhibition leads to expression of both major histocompatibility complex class I and II (MHCI/II) expression at both the mRNA and protein levels. ChIP-sequencing confirmed loss of EZH2-mediated histone marks and gain of activating histone marks at key loci. Further, we demonstrate strong tumor control in models of both autochthonous and syngeneic LSCC treated with anti-PD1 immunotherapy with EZH2 inhibition. Single-cell RNA sequencing and immune cell profiling demonstrated phenotypic changes towards more tumor suppressive phenotypes in EZH2 inhibitor treated tumors. These results indicate that this therapeutic modality could increase ICI responses in patients undergoing treatment for LSCC.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Targeting ULK1 Decreases IFNγ-Mediated Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.
In Molecular Cancer Research on 1 April 2023 by Fenton, S. E., Zannikou, M., et al.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have transformed the treatment of melanoma. However, the majority of patients have primary or acquired resistance to ICIs, limiting durable responses and patient survival. IFNγ signaling and the expression of IFNγ-stimulated genes correlate with either response or resistance to ICIs, in a context-dependent manner. While IFNγ-inducible immunostimulatory genes are required for response to ICIs, chronic IFNγ signaling induces the expression of immunosuppressive genes, promoting resistance to these therapies. Here, we show that high levels of Unc-51 like kinase 1 (ULK1) correlate with poor survival in patients with melanoma and overexpression of ULK1 in melanoma cells enhances IFNγ-induced expression of immunosuppressive genes, with minimal effects on the expression of immunostimulatory genes. In contrast, genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of ULK1 reduces expression of IFNγ-induced immunosuppressive genes. ULK1 binds IRF1 in the nuclear compartment of melanoma cells, controlling its binding to the programmed death-ligand 1 promoter region. In addition, pharmacologic inhibition of ULK1 in combination with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 therapy further reduces melanoma tumor growth in vivo. Our data suggest that targeting ULK1 represses IFNγ-dependent immunosuppression. These findings support the combination of ULK1 drug-targeted inhibition with ICIs for the treatment of patients with melanoma to improve response rates and patient outcomes. This study identifies ULK1, activated downstream of IFNγ signaling, as a druggable target to overcome resistance mechanisms to ICI therapy in metastatic melanoma. ©2022 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Pharmacology
Pexidartinib synergize PD-1 antibody through inhibiting treg infiltration by reducing TAM-derived CCL22 in lung adenocarcinoma.
In Frontiers in Pharmacology on 28 March 2023 by Zhang, W., Jiang, X., et al.
There is a crosstalk between Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) and tumor-infiltrating T cells in tumor environment. TAM could inhibit the activity of cytotoxic T cells; TAM could also regulate the composition of T cells in tumor immune environment. The combination therapy for TAM and tumor infiltrated T cells has been widely noticed, but the crosstalk between TAM and tumor infiltrated T cells remains unclear in the process of combination therapy. We treated lung adenocarcinoma tumor models with pexidartinib, which targets macrophage colony stimulating factor receptor (M-CSFR) and c-kit tyrosine kinase, to inhibited TAM. Pexidartinib inhibited the ratio of macrophages in the tumor and also altered macrophage polarization. In addition to reprogram TAM, pexidartinib also changed the composition of tumor-invasive T cells. After pexidartinib treatment, the total number of T cells, CD8+ T cells and Treg cells were all decreased, the ratio of CD8+T/Treg increased significantly. According to the analysis of cytokines and chemokines during the treatment of pexidartinib, CCL22, as a chemokine for Treg recruitment, significantly decreased after the treatment of pexidartinib. Base on the above observation, the combination of pexidartinib and PD-1 antibody were used in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma subcutaneous tumor model, the combination therapy has significantly improved the efficacy of tumor treatment compared with the monotherapy. Meanwhile, compared with pexidartinib monotherapy, the combination treatment further switches the polarization status of tumor-associated macrophages. In summary, our results showed that the combination of pexidartinib and PD-1 antibody showed a synergy and significantly improved the anti-tumor efficacy, through pexidartinib increasing CD8T/Treg ratio by reducing TAM-derived CCL22. Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Jiang, Zou, Yuan and Wang.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Adhesion analysis via a tumor vasculature-like microfluidic device identifies CD8+ T cells with enhanced tumor homing to improve cell therapy.
In Cell Reports on 28 March 2023 by Camargo, C. P., Muhuri, A. K., et al.
CD8+ T cell recruitment to the tumor microenvironment is critical for the success of adoptive cell therapy (ACT). Unfortunately, only a small fraction of transferred cells home to solid tumors. Adhesive ligand-receptor interactions have been implicated in CD8+ T cell homing; however, there is a lack of understanding of how CD8+ T cells interact with tumor vasculature-expressed adhesive ligands under the influence of hemodynamic flow. Here, the capacity of CD8+ T cells to home to melanomas is modeled ex vivo using an engineered microfluidic device that recapitulates the hemodynamic microenvironment of the tumor vasculature. Adoptively transferred CD8+ T cells with enhanced adhesion in flow in vitro and tumor homing in vivo improve tumor control by ACT in combination with immune checkpoint blockade. These results show that engineered microfluidic devices can model the microenvironment of the tumor vasculature to identify subsets of T cells with enhanced tumor infiltrating capabilities, a key limitation in ACT. Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
-
-
In Vivo
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
Tumor PD-L1 engages myeloid PD-1 to suppress type I interferon to impair cytotoxic T lymphocyte recruitment.
In Cancer Cell on 13 March 2023 by Klement, J. D., Redd, P. S., et al.
The cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying tumor cell PD-L1 (tPD-L1) function in tumor immune evasion are incompletely understood. We report here that tPD-L1 does not suppress cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activity in co-cultures of tumor cells and tumor-specific CTLs and exhibits no effect on primary tumor growth. However, deleting tPD-L1 decreases lung metastasis in a CTL-dependent manner in tumor-bearing mice. Depletion of myeloid cells or knocking out PD-1 in myeloid cells (mPD-1) impairs tPD-L1 promotion of tumor lung metastasis in mice. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) reveals that tPD-L1 engages mPD-1 to activate SHP2 to antagonize the type I interferon (IFN-I) and STAT1 pathway to repress Cxcl9 and impair CTL recruitment to lung metastases. Human cancer patient response to PD-1 blockade immunotherapy correlates with IFN-I response in myeloid cells. Our findings determine that tPD-L1 engages mPD-1 to activate SHP2 to suppress the IFN-I-STAT1-CXCL9 pathway to impair CTL tumor recruitment in lung metastasis. Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-