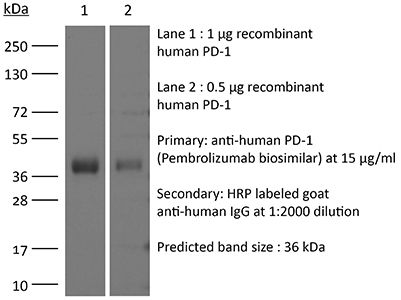
InVivoSIM anti-human PD-1 (Pembrolizumab Biosimilar)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Human IgG4 |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb human IgG4 (S228P) isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Mutations | S228P |
| Immunogen | Human PD-1 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling in vitro functional assay |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Aggregation* | <5%, Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2894731 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Lee DH, Ahn H, Sim HI, Choi E, Choi S, Jo Y, Yun B, Song HK, Oh SJ, Denda-Nagai K, Park CS, Irimura T, Park Y, Jin HS (2023). "A CRISPR activation screen identifies MUC-21 as critical for resistance to NK and T cell-mediated cytotoxicity" J Exp Clin
PubMed
Background: Immunotherapy has significantly advanced cancer treatments, but many patients do not respond to it, partly due to immunosuppressive mechanisms used by tumor cells. These cells employ immunosuppressive ligands to evade detection and elimination by the immune system. Therefore, the discovery and characterization of novel immunosuppressive ligands that facilitate immune evasion are crucial for developing more potent anti-cancer therapies. Methods: We conducted gain-of-function screens using a CRISPRa (CRISPR activation) library that covered the entire human transmembrane sub-genome to identify surface molecules capable of hindering NK-mediated cytotoxicity. The immunosuppressive role and mechanism of MUC21 were validated using NK and T cell mediated cytotoxicity assays. Bioinformatics tools were employed to assess the clinical implications of mucin-21 (MUC21) in cancer cell immunity. Results: Our genetic screens revealed that MUC21 expression on cancer cell surfaces inhibits both the cytotoxic activity of NK cells and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, but not affecting complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Additionally, MUC21 expression hinders T cell activation by impeding antigen recognition, thereby diminishing the effectiveness of the immune checkpoint inhibitor, anti-PD-L1. Moreover, MUC21 expression suppress the antitumor function of both CAR-T cells and CAR-NK cells. Mechanistically, MUC21 facilitates immune evasion by creating steric hindrance, preventing interactions between cancer and immune cells. Bioinformatics analysis revealed elevated MUC21 expression in lung cancer, which correlated with reduced infiltration and activation of cytotoxic immune cells. Intriguingly, MUC21 expression was higher in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumors that were non-responsive to anti-PD-(L)1 treatment compared to responsive tumors. Conclusions: These findings indicate that surface MUC21 serves as a potent immunosuppressive ligand, shielding cancer cells from NK and CD8+T cell attacks. This suggests that inhibiting MUC21 could be a promising strategy to improve cancer immunotherapy.
in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Myers Chen K, Grun D, Gautier B, Venkatesha S, Maddox M, Zhang AH, Andersen P (2024). "Targeting PD-L1 in solid cancer with myeloid cells expressing a CAR-like immune receptor" Front Immunol .
PubMed
Introduction: Solid cancers Myeloid cells are prevalent in solid cancers, but they frequently exhibit an anti-inflammatory pro-tumor phenotype that contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME), which hinders the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapies. Myeloid cells' natural ability of tumor trafficking makes engineered myeloid cell therapy an intriguing approach to tackle the challenges posed by solid cancers, including tumor infiltration, tumor cell heterogenicity and the immunosuppressive TME. One such engineering approach is to target the checkpoint molecule PD-L1, which is often upregulated by solid cancers to evade immune responses. Method: Here we devised an adoptive cell therapy strategy based on myeloid cells expressing a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-like immune receptor (CARIR). The extracellular domain of CARIR is derived from the natural inhibitory receptor PD-1, while the intracellular domain(s) are derived from CD40 and/or CD3ζ. To assess the efficacy of CARIR-engineered myeloid cells, we conducted proof-of-principle experiments using co-culture and flow cytometry-based phagocytosis assays in vitro. Additionally, we employed a fully immune-competent syngeneic tumor mouse model to evaluate the strategy's effectiveness in vivo. Result: Co-culturing CARIR-expressing human monocytic THP-1 cells with PD-L1 expressing target cells lead to upregulation of the costimulatory molecule CD86 along with expression of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-1α and IL-1β. Moreover, CARIR expression significantly enhanced phagocytosis of multiple PD-L1 expressing cancer cell lines in vitro. Similar outcomes were observed with CARIR-expressing human primary macrophages. In experiments conducted in syngeneic BALB/c mice bearing 4T1 mammary tumors, infusing murine myeloid cells that express a murine version of CARIR significantly slowed tumor growth and prolonged survival. Conclusion: Taken together, these results demonstrate that adoptive transfer of PD-1 CARIR-engineered myeloid cells represents a promising strategy for treating PD-L1 positive solid cancers.
in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Rafiei A, Gualandi M, Yang CL, Woods R, Kumar A, Brunner K, Sigrist J, Ebersbach H, Coats S, Renner C, Marroquin Belaunzaran O (2024). "IOS-1002, a Stabilized HLA-B57 Open Format, Exerts Potent Anti-Tumor Activity" Cancers (Basel) 16(16):2902.
PubMed
HLA-B27 and HLA-B57 are associated with autoimmunity and long-term viral control and protection against HIV and HCV infection; however, their role in cancer immunity remains unknown. HLA class I molecules interact with innate checkpoint receptors of the LILRA, LILRB and KIR families present in diverse sets of immune cells. Here, we demonstrate that an open format (peptide free conformation) and expression- and stability-optimized HLA-B57-B2m-IgG4_Fc fusion protein (IOS-1002) binds to human leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B1 and B2 (LILRB1 and LILRB2) and to killer immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL1 (KIR3DL1). In addition, we show that the IgG4 Fc backbone is required for engagement to Fcγ receptors and potent activation of macrophage phagocytosis. IOS-1002 blocks the immunosuppressive ITIM and SHP1/2 phosphatase signaling cascade, reduces the expression of immunosuppressive M2-like polarization markers of macrophages and differentiation of monocytes to myeloid-derived suppressor cells, enhances tumor cell phagocytosis in vitro and potentiates activation of T and NK cells. Lastly, IOS-1002 demonstrates efficacy in an ex vivo patient-derived tumor sample tumoroid model. IOS-1002 is a first-in-class multi-target and multi-functional human-derived HLA molecule that activates anti-tumor immunity and is currently under clinical evaluation.
in vitro functional assay
Sun Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, Yi D, Kong F, Zhao L, Liao D, Chen L, Ma Q, Wang Z (2024). "ADCY4 promotes brain metastasis in small cell lung cancer and is associated with energy metabolism" Heliyon 10(7):e28162.
PubMed
Brain metastasis (BMs) in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) has a very poor prognosis. This study combined WGCNA with the mfuzz algorithm to identify potential biomarkers in the peripheral blood of patients with BMs. By comparing the significantly differentially expressed genes present in BMs samples, we identified ADCY4 as a target for further study. Expression of ADCY4 was used to cluster mfuzz expression pattern, and 28 hub genes for functional enrichment. PPI network analysis were obtained by comparing with differentially expressed genes in BMs. GABRE, NFE4 and LMOD2 are highly expressed in patients with BMs and have a good diagnostic effect. Immunoinfiltration analysis showed that SCLC patients with BMs may be associated with memory B cells, Tregs, NK cell activation, macrophage M0 and dendritic cell activation. prophytic was used to investigate the ADCY4-mediated anti-tumor drug response. In conclusion, ADCY4 can be used as a promising candidate biomarker for predicting BMs, molecular and immune features in SCLC. PCR showed that ADCY4 expression was increased in NCI-H209 and NCI-H526 SCLC cell lines. In vitro experiments confirmed that the expression of ADCY4 was significantly decreased after anti-PD1 antibody treatment, while the expression of energy metabolism factors were significantly different. This study reveals a potential mechanism by which ADCY4 mediates poor prognosis through energy metabolism -related pathways in SCLC.
in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Wang C, He L, Peng J, Lu C, Zhang M, Qi X, Zhang M, Wang Y (2024). "Identification of Siglec-10 as a new dendritic cell checkpoint for cervical cancer immunotherapy" J Immunother Cancer 12(8):e009404.
PubMed
Background: The occurrence of chronic inflammation resulting from infection with human papillomaviruses is an important factor in the development of cervical cancer (CC); thus, deciphering the crosstalk between the tumor microenvironment and innate immune cells during the establishment of immune tolerance is vital for identifying potential treatment strategies. Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing data and primary tumor samples from patients with CC were used to evaluate the functional role of Siglec-10 on dendritic cells (DCs). Patient-derived tumor fragment platforms were used to examine the ability of Siglec-10 blockade to reinvigorate DC-mediate T-cell activation and tumor clearance. Results: Here, we demonstrated that Siglec-10 is a prominent inhibitory checkpoint for DCs infiltrated in CC. CC epithelial cells use their aberrant surface sialylated structures to induce the transformation of conventional DCs into phenotypes characterized by low immunogenicity and high immunotolerance. Additionally, Siglec-10+ DCs suppress the function of adaptive T cells via galectin-9 signaling to strengthen the immunosuppressive CC microenvironment. Disturbance of Siglec-10 signaling restored the DC-mediated tumoricidal response and increased adaptive T cells sensitivity to programmed cell death protein 1 inhibition. Conclusion: Our study confirms the checkpoint role of Siglec-10 on DCs and proposes that targeting Siglec-10 may be a promising avenue for immunotherapy against CC.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Liang M, Sun Z, Chen X, Wang L, Wang H, Qin L, Zhao W, Geng B (2023). "E3 ligase TRIM28 promotes anti-PD-1 resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by enhancing the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells" J Exp Clin Cancer Res 42(1):275.
PubMed
Background: Alterations in several tripartite motif-containing (TRIM) family proteins have been implicated in the pathogenesis of lung cancer. TRIM28, a member of the TRIM E3 ligase family, has been associated with tumorigenesis, cell proliferation, and inflammation. However, little is known about TRIM28 expression and its role in the immune microenvironment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Methods: We assessed the clinical significance of TRIM28 in tissue microarrays and TCGA cohorts. We investigated the function of TRIM28 in syngeneic mouse tumor models, the KrasLSL-G12D/+; Tp53fl/fl (KP) mouse model, and humanized mice. Immune cell composition was analyzed using flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry. Results: Our findings revealed a positive correlation between TRIM28 expression and the infiltration of suppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in NSCLC. Moreover, silencing TRIM28 enhanced the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by reshaping the inflamed tumor microenvironment. Mechanistically, we demonstrated that TRIM28 could physically interact with receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and promote K63-linked ubiquitination of RIPK1, which is crucial for sustaining activation of the NF-κB pathway. Mutagenesis of the E3 ligase domain corroborated the essential role of E3 ligase activity in TRIM28-mediated NF-κB activation. Further experiments revealed that TRIM28 could upregulate the expression of CXCL1 by activating NF-κB signaling. CXCL1 could bind to CXCR2 on MDSCs and promote their migration to the tumor microenvironment. TRIM28 knockdown increased responsiveness to anti-PD-1 therapy in immunocompetent mice, characterized by increased CD8+T tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and decreased MDSCs. Conclusion: The present study identified TRIM28 as a promoter of chemokine-driven recruitment of MDSCs through RIPK1-mediated NF-κB activation, leading to the suppression of infiltrating activated CD8+T cells and the development of anti-PD-1 resistance. Understanding the regulation of MDSC recruitment and function by TRIM28 provides crucial insights into the association between TRIM28 signaling and the development of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. These insights may inform the development of combination therapies to enhance the effectiveness of immune checkpoint blockade therapy in NSCLC.
in vitro functional assay
Dong H, He X, Zhang L, Chen W, Lin YC, Liu SB, Wang H, Nguyen LXT, Li M, Zhu Y, Zhao D, Ghoda L, Serody J, Vincent B, Luznik L, Gojo I, Zeidner J, Su R, Chen J, Sharma R, Pirrotte P, Wu X, Hu W, Han W, Shen B, Kuo YH, Jin J, Salhotra A, Wang J, Marcu
PubMed
Current anticancer therapies cannot eliminate all cancer cells, which hijack normal arginine methylation as a means to promote their maintenance via unknown mechanisms. Here we show that targeting protein arginine N-methyltransferase 9 (PRMT9), whose activities are elevated in blasts and leukemia stem cells (LSCs) from patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), eliminates disease via cancer-intrinsic mechanisms and cancer-extrinsic type I interferon (IFN)-associated immunity. PRMT9 ablation in AML cells decreased the arginine methylation of regulators of RNA translation and the DNA damage response, suppressing cell survival. Notably, PRMT9 inhibition promoted DNA damage and activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, which underlies the type I IFN response. Genetically activating cyclic GMP-AMP synthase in AML cells blocked leukemogenesis. We also report synergy of a PRMT9 inhibitor with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 in eradicating AML. Overall, we conclude that PRMT9 functions in survival and immune evasion of both LSCs and non-LSCs; targeting PRMT9 may represent a potential anticancer strategy.
in vivo PD-1 blockade in humanized mice
Choi B, Lee JS, Kim SJ, Hong D, Park JB, Lee KY (2020). "Anti-tumor effects of anti-PD-1 antibody, pembrolizumab, in humanized NSG PDX mice xenografted with dedifferentiated liposarcoma" Cancer Lett .
PubMed
The efficacy of an immune checkpoint blockade has been demonstrated against various types of cancer, but its suitability has not been fully proven for therapies specifically targeting sarcoma. We conducted a pan-cancer tumor data analysis to identify key immune-related variables strongly associated with sarcoma prognosis, and we explored whether these expected factors are functionally correlated with anti-PD-1 therapy in humanized (Hu) NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice xenografted with dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDLPS). We found that an abundance of hCD8+ T cells and hNK cells was functionally associated with anti-PD-1 effects in the Hu-NSG DDLPS mice. Phenotypically, these cells were shown to be hCD8+IFNγ+, hCD8+PD-1+, hCD8+Ki-67+, hCD56+IFNγ+, hCD56+PD-1+, and hCD56+Ki-67+ cells and were enriched in splenocytes and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) of Hu-NSG DDLPS mice treated with anti-PD-1 antibody. Moreover, a considerable increase in activated hCD56+NKp46+NKG2D+ NK cells was also detected. Our findings suggest that hCD8+ T and hNK subsets play a pivotal role in anti-DDLPS tumor effects of anti-PD-1 therapy. The results provide clinical reference for advanced anti-PD-1 therapy targeting sarcoma tumors including DDLPS.
in vitro functional assay
Dong H, He X, Zhang L, Chen W, Lin YC, Liu SB, Wang H, Nguyen LXT, Li M, Zhu Y, Zhao D, Ghoda L, Serody J, Vincent B, Luznik L, Gojo I, Zeidner J, Su R, Chen J, Sharma R, Pirrotte P, Wu X, Hu W, Han W, Shen B, Kuo YH, Jin J, Salhotra A, Wang J, Marcu
PubMed
Current anticancer therapies cannot eliminate all cancer cells, which hijack normal arginine methylation as a means to promote their maintenance via unknown mechanisms. Here we show that targeting protein arginine N-methyltransferase 9 (PRMT9), whose activities are elevated in blasts and leukemia stem cells (LSCs) from patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), eliminates disease via cancer-intrinsic mechanisms and cancer-extrinsic type I interferon (IFN)-associated immunity. PRMT9 ablation in AML cells decreased the arginine methylation of regulators of RNA translation and the DNA damage response, suppressing cell survival. Notably, PRMT9 inhibition promoted DNA damage and activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, which underlies the type I IFN response. Genetically activating cyclic GMP-AMP synthase in AML cells blocked leukemogenesis. We also report synergy of a PRMT9 inhibitor with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 in eradicating AML. Overall, we conclude that PRMT9 functions in survival and immune evasion of both LSCs and non-LSCs; targeting PRMT9 may represent a potential anticancer strategy.
in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Wang C, He L, Peng J, Lu C, Zhang M, Qi X, Zhang M, Wang Y (2024). "Identification of Siglec-10 as a new dendritic cell checkpoint for cervical cancer immunotherapy" J Immunother Cancer 12(8):e009404.
PubMed
Background: The occurrence of chronic inflammation resulting from infection with human papillomaviruses is an important factor in the development of cervical cancer (CC); thus, deciphering the crosstalk between the tumor microenvironment and innate immune cells during the establishment of immune tolerance is vital for identifying potential treatment strategies. Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing data and primary tumor samples from patients with CC were used to evaluate the functional role of Siglec-10 on dendritic cells (DCs). Patient-derived tumor fragment platforms were used to examine the ability of Siglec-10 blockade to reinvigorate DC-mediate T-cell activation and tumor clearance. Results: Here, we demonstrated that Siglec-10 is a prominent inhibitory checkpoint for DCs infiltrated in CC. CC epithelial cells use their aberrant surface sialylated structures to induce the transformation of conventional DCs into phenotypes characterized by low immunogenicity and high immunotolerance. Additionally, Siglec-10+ DCs suppress the function of adaptive T cells via galectin-9 signaling to strengthen the immunosuppressive CC microenvironment. Disturbance of Siglec-10 signaling restored the DC-mediated tumoricidal response and increased adaptive T cells sensitivity to programmed cell death protein 1 inhibition. Conclusion: Our study confirms the checkpoint role of Siglec-10 on DCs and proposes that targeting Siglec-10 may be a promising avenue for immunotherapy against CC.
in vitro functional assay
Sun Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, Yi D, Kong F, Zhao L, Liao D, Chen L, Ma Q, Wang Z (2024). "ADCY4 promotes brain metastasis in small cell lung cancer and is associated with energy metabolism" Heliyon 10(7):e28162.
PubMed
Brain metastasis (BMs) in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) has a very poor prognosis. This study combined WGCNA with the mfuzz algorithm to identify potential biomarkers in the peripheral blood of patients with BMs. By comparing the significantly differentially expressed genes present in BMs samples, we identified ADCY4 as a target for further study. Expression of ADCY4 was used to cluster mfuzz expression pattern, and 28 hub genes for functional enrichment. PPI network analysis were obtained by comparing with differentially expressed genes in BMs. GABRE, NFE4 and LMOD2 are highly expressed in patients with BMs and have a good diagnostic effect. Immunoinfiltration analysis showed that SCLC patients with BMs may be associated with memory B cells, Tregs, NK cell activation, macrophage M0 and dendritic cell activation. prophytic was used to investigate the ADCY4-mediated anti-tumor drug response. In conclusion, ADCY4 can be used as a promising candidate biomarker for predicting BMs, molecular and immune features in SCLC. PCR showed that ADCY4 expression was increased in NCI-H209 and NCI-H526 SCLC cell lines. In vitro experiments confirmed that the expression of ADCY4 was significantly decreased after anti-PD1 antibody treatment, while the expression of energy metabolism factors were significantly different. This study reveals a potential mechanism by which ADCY4 mediates poor prognosis through energy metabolism -related pathways in SCLC.
in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Rafiei A, Gualandi M, Yang CL, Woods R, Kumar A, Brunner K, Sigrist J, Ebersbach H, Coats S, Renner C, Marroquin Belaunzaran O (2024). "IOS-1002, a Stabilized HLA-B57 Open Format, Exerts Potent Anti-Tumor Activity" Cancers (Basel) 16(16):2902.
PubMed
HLA-B27 and HLA-B57 are associated with autoimmunity and long-term viral control and protection against HIV and HCV infection; however, their role in cancer immunity remains unknown. HLA class I molecules interact with innate checkpoint receptors of the LILRA, LILRB and KIR families present in diverse sets of immune cells. Here, we demonstrate that an open format (peptide free conformation) and expression- and stability-optimized HLA-B57-B2m-IgG4_Fc fusion protein (IOS-1002) binds to human leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B1 and B2 (LILRB1 and LILRB2) and to killer immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL1 (KIR3DL1). In addition, we show that the IgG4 Fc backbone is required for engagement to Fcγ receptors and potent activation of macrophage phagocytosis. IOS-1002 blocks the immunosuppressive ITIM and SHP1/2 phosphatase signaling cascade, reduces the expression of immunosuppressive M2-like polarization markers of macrophages and differentiation of monocytes to myeloid-derived suppressor cells, enhances tumor cell phagocytosis in vitro and potentiates activation of T and NK cells. Lastly, IOS-1002 demonstrates efficacy in an ex vivo patient-derived tumor sample tumoroid model. IOS-1002 is a first-in-class multi-target and multi-functional human-derived HLA molecule that activates anti-tumor immunity and is currently under clinical evaluation.
in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Myers Chen K, Grun D, Gautier B, Venkatesha S, Maddox M, Zhang AH, Andersen P (2024). "Targeting PD-L1 in solid cancer with myeloid cells expressing a CAR-like immune receptor" Front Immunol .
PubMed
Introduction: Solid cancers Myeloid cells are prevalent in solid cancers, but they frequently exhibit an anti-inflammatory pro-tumor phenotype that contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME), which hinders the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapies. Myeloid cells' natural ability of tumor trafficking makes engineered myeloid cell therapy an intriguing approach to tackle the challenges posed by solid cancers, including tumor infiltration, tumor cell heterogenicity and the immunosuppressive TME. One such engineering approach is to target the checkpoint molecule PD-L1, which is often upregulated by solid cancers to evade immune responses. Method: Here we devised an adoptive cell therapy strategy based on myeloid cells expressing a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-like immune receptor (CARIR). The extracellular domain of CARIR is derived from the natural inhibitory receptor PD-1, while the intracellular domain(s) are derived from CD40 and/or CD3ζ. To assess the efficacy of CARIR-engineered myeloid cells, we conducted proof-of-principle experiments using co-culture and flow cytometry-based phagocytosis assays in vitro. Additionally, we employed a fully immune-competent syngeneic tumor mouse model to evaluate the strategy's effectiveness in vivo. Result: Co-culturing CARIR-expressing human monocytic THP-1 cells with PD-L1 expressing target cells lead to upregulation of the costimulatory molecule CD86 along with expression of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-1α and IL-1β. Moreover, CARIR expression significantly enhanced phagocytosis of multiple PD-L1 expressing cancer cell lines in vitro. Similar outcomes were observed with CARIR-expressing human primary macrophages. In experiments conducted in syngeneic BALB/c mice bearing 4T1 mammary tumors, infusing murine myeloid cells that express a murine version of CARIR significantly slowed tumor growth and prolonged survival. Conclusion: Taken together, these results demonstrate that adoptive transfer of PD-1 CARIR-engineered myeloid cells represents a promising strategy for treating PD-L1 positive solid cancers.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Yu W, He J, Wang F, He Q, Shi Y, Tao X, Sun B (2023). "NR4A1 mediates NK-cell dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma via the IFN-γ/p-STAT1/IRF1 pathway" Immunology 169(1):69-82.
PubMed
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most fatal tumours worldwide and has a high recurrence rate. Nevertheless, the mechanism of HCC genesis remains partly unexplored, while the efficiency of HCC treatments remains limited. The present study analysed the expression of nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (NR4A1) in tumour-infiltrating natural killer (NK) cells derived from both human patients with HCC and tumour-bearing mouse models, as well as the features of NR4A1high and NR4A1low NK cells. In addition, knockout of NR4A1 by CRISPR/Cas9 and adoptive transfer experiments were applied to verify the function of NR4A1 in both tumour-infiltrating NK cells and anti-PD-1 therapy. The present study found that NR4A1 was significantly highly expressed in tumour-infiltrating NK cells, which mediated the dysfunction of tumour-infiltrating NK cells by regulating the IFN-γ/p-STAT1/IRF1 signalling pathway. Knockout of NR4A1 in NK cells not only restored the antitumour function of NK cells but also enhanced the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy. The present findings suggest a regulatory role of NR4A1 in the immune progress of NK cells against HCC, which may provide a new direction for immunotherapies of HCC.
in vitro blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Lee DH, Ahn H, Sim HI, Choi E, Choi S, Jo Y, Yun B, Song HK, Oh SJ, Denda-Nagai K, Park CS, Irimura T, Park Y, Jin HS (2023). "A CRISPR activation screen identifies MUC-21 as critical for resistance to NK and T cell-mediated cytotoxicity" J Exp Clin
PubMed
Background: Immunotherapy has significantly advanced cancer treatments, but many patients do not respond to it, partly due to immunosuppressive mechanisms used by tumor cells. These cells employ immunosuppressive ligands to evade detection and elimination by the immune system. Therefore, the discovery and characterization of novel immunosuppressive ligands that facilitate immune evasion are crucial for developing more potent anti-cancer therapies. Methods: We conducted gain-of-function screens using a CRISPRa (CRISPR activation) library that covered the entire human transmembrane sub-genome to identify surface molecules capable of hindering NK-mediated cytotoxicity. The immunosuppressive role and mechanism of MUC21 were validated using NK and T cell mediated cytotoxicity assays. Bioinformatics tools were employed to assess the clinical implications of mucin-21 (MUC21) in cancer cell immunity. Results: Our genetic screens revealed that MUC21 expression on cancer cell surfaces inhibits both the cytotoxic activity of NK cells and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, but not affecting complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Additionally, MUC21 expression hinders T cell activation by impeding antigen recognition, thereby diminishing the effectiveness of the immune checkpoint inhibitor, anti-PD-L1. Moreover, MUC21 expression suppress the antitumor function of both CAR-T cells and CAR-NK cells. Mechanistically, MUC21 facilitates immune evasion by creating steric hindrance, preventing interactions between cancer and immune cells. Bioinformatics analysis revealed elevated MUC21 expression in lung cancer, which correlated with reduced infiltration and activation of cytotoxic immune cells. Intriguingly, MUC21 expression was higher in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumors that were non-responsive to anti-PD-(L)1 treatment compared to responsive tumors. Conclusions: These findings indicate that surface MUC21 serves as a potent immunosuppressive ligand, shielding cancer cells from NK and CD8+T cell attacks. This suggests that inhibiting MUC21 could be a promising strategy to improve cancer immunotherapy.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Yu W, He J, Wang F, He Q, Shi Y, Tao X, Sun B (2023). "NR4A1 mediates NK-cell dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma via the IFN-γ/p-STAT1/IRF1 pathway" Immunology 169(1):69-82.
PubMed
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most fatal tumours worldwide and has a high recurrence rate. Nevertheless, the mechanism of HCC genesis remains partly unexplored, while the efficiency of HCC treatments remains limited. The present study analysed the expression of nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (NR4A1) in tumour-infiltrating natural killer (NK) cells derived from both human patients with HCC and tumour-bearing mouse models, as well as the features of NR4A1high and NR4A1low NK cells. In addition, knockout of NR4A1 by CRISPR/Cas9 and adoptive transfer experiments were applied to verify the function of NR4A1 in both tumour-infiltrating NK cells and anti-PD-1 therapy. The present study found that NR4A1 was significantly highly expressed in tumour-infiltrating NK cells, which mediated the dysfunction of tumour-infiltrating NK cells by regulating the IFN-γ/p-STAT1/IRF1 signalling pathway. Knockout of NR4A1 in NK cells not only restored the antitumour function of NK cells but also enhanced the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy. The present findings suggest a regulatory role of NR4A1 in the immune progress of NK cells against HCC, which may provide a new direction for immunotherapies of HCC.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Liang M, Sun Z, Chen X, Wang L, Wang H, Qin L, Zhao W, Geng B (2023). "E3 ligase TRIM28 promotes anti-PD-1 resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by enhancing the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells" J Exp Clin Cancer Res 42(1):275.
PubMed
Background: Alterations in several tripartite motif-containing (TRIM) family proteins have been implicated in the pathogenesis of lung cancer. TRIM28, a member of the TRIM E3 ligase family, has been associated with tumorigenesis, cell proliferation, and inflammation. However, little is known about TRIM28 expression and its role in the immune microenvironment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Methods: We assessed the clinical significance of TRIM28 in tissue microarrays and TCGA cohorts. We investigated the function of TRIM28 in syngeneic mouse tumor models, the KrasLSL-G12D/+; Tp53fl/fl (KP) mouse model, and humanized mice. Immune cell composition was analyzed using flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry. Results: Our findings revealed a positive correlation between TRIM28 expression and the infiltration of suppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in NSCLC. Moreover, silencing TRIM28 enhanced the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by reshaping the inflamed tumor microenvironment. Mechanistically, we demonstrated that TRIM28 could physically interact with receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and promote K63-linked ubiquitination of RIPK1, which is crucial for sustaining activation of the NF-κB pathway. Mutagenesis of the E3 ligase domain corroborated the essential role of E3 ligase activity in TRIM28-mediated NF-κB activation. Further experiments revealed that TRIM28 could upregulate the expression of CXCL1 by activating NF-κB signaling. CXCL1 could bind to CXCR2 on MDSCs and promote their migration to the tumor microenvironment. TRIM28 knockdown increased responsiveness to anti-PD-1 therapy in immunocompetent mice, characterized by increased CD8+T tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and decreased MDSCs. Conclusion: The present study identified TRIM28 as a promoter of chemokine-driven recruitment of MDSCs through RIPK1-mediated NF-κB activation, leading to the suppression of infiltrating activated CD8+T cells and the development of anti-PD-1 resistance. Understanding the regulation of MDSC recruitment and function by TRIM28 provides crucial insights into the association between TRIM28 signaling and the development of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. These insights may inform the development of combination therapies to enhance the effectiveness of immune checkpoint blockade therapy in NSCLC.
in vivo PD-1 blockade in humanized mice
Choi B, Lee JS, Kim SJ, Hong D, Park JB, Lee KY (2020). "Anti-tumor effects of anti-PD-1 antibody, pembrolizumab, in humanized NSG PDX mice xenografted with dedifferentiated liposarcoma" Cancer Lett .
PubMed
The efficacy of an immune checkpoint blockade has been demonstrated against various types of cancer, but its suitability has not been fully proven for therapies specifically targeting sarcoma. We conducted a pan-cancer tumor data analysis to identify key immune-related variables strongly associated with sarcoma prognosis, and we explored whether these expected factors are functionally correlated with anti-PD-1 therapy in humanized (Hu) NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice xenografted with dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDLPS). We found that an abundance of hCD8+ T cells and hNK cells was functionally associated with anti-PD-1 effects in the Hu-NSG DDLPS mice. Phenotypically, these cells were shown to be hCD8+IFNγ+, hCD8+PD-1+, hCD8+Ki-67+, hCD56+IFNγ+, hCD56+PD-1+, and hCD56+Ki-67+ cells and were enriched in splenocytes and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) of Hu-NSG DDLPS mice treated with anti-PD-1 antibody. Moreover, a considerable increase in activated hCD56+NKp46+NKG2D+ NK cells was also detected. Our findings suggest that hCD8+ T and hNK subsets play a pivotal role in anti-DDLPS tumor effects of anti-PD-1 therapy. The results provide clinical reference for advanced anti-PD-1 therapy targeting sarcoma tumors including DDLPS.
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
E3 ligase TRIM28 promotes anti-PD-1 resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by enhancing the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells.
In Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR on 21 October 2023 by Liang, M., Sun, Z., et al.
Alterations in several tripartite motif-containing (TRIM) family proteins have been implicated in the pathogenesis of lung cancer. TRIM28, a member of the TRIM E3 ligase family, has been associated with tumorigenesis, cell proliferation, and inflammation. However, little is known about TRIM28 expression and its role in the immune microenvironment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We assessed the clinical significance of TRIM28 in tissue microarrays and TCGA cohorts. We investigated the function of TRIM28 in syngeneic mouse tumor models, the KrasLSL-G12D/+; Tp53fl/fl (KP) mouse model, and humanized mice. Immune cell composition was analyzed using flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry. Our findings revealed a positive correlation between TRIM28 expression and the infiltration of suppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in NSCLC. Moreover, silencing TRIM28 enhanced the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by reshaping the inflamed tumor microenvironment. Mechanistically, we demonstrated that TRIM28 could physically interact with receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and promote K63-linked ubiquitination of RIPK1, which is crucial for sustaining activation of the NF-κB pathway. Mutagenesis of the E3 ligase domain corroborated the essential role of E3 ligase activity in TRIM28-mediated NF-κB activation. Further experiments revealed that TRIM28 could upregulate the expression of CXCL1 by activating NF-κB signaling. CXCL1 could bind to CXCR2 on MDSCs and promote their migration to the tumor microenvironment. TRIM28 knockdown increased responsiveness to anti-PD-1 therapy in immunocompetent mice, characterized by increased CD8+T tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and decreased MDSCs. The present study identified TRIM28 as a promoter of chemokine-driven recruitment of MDSCs through RIPK1-mediated NF-κB activation, leading to the suppression of infiltrating activated CD8+T cells and the development of anti-PD-1 resistance. Understanding the regulation of MDSC recruitment and function by TRIM28 provides crucial insights into the association between TRIM28 signaling and the development of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. These insights may inform the development of combination therapies to enhance the effectiveness of immune checkpoint blockade therapy in NSCLC. © 2023. Italian National Cancer Institute ‘Regina Elena’.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
NR4A1 mediates NK-cell dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma via the IFN-γ/p-STAT1/IRF1 pathway.
In Immunology on 1 May 2023 by Yu, W., He, J., et al.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most fatal tumours worldwide and has a high recurrence rate. Nevertheless, the mechanism of HCC genesis remains partly unexplored, while the efficiency of HCC treatments remains limited. The present study analysed the expression of nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (NR4A1) in tumour-infiltrating natural killer (NK) cells derived from both human patients with HCC and tumour-bearing mouse models, as well as the features of NR4A1high and NR4A1low NK cells. In addition, knockout of NR4A1 by CRISPR/Cas9 and adoptive transfer experiments were applied to verify the function of NR4A1 in both tumour-infiltrating NK cells and anti-PD-1 therapy. The present study found that NR4A1 was significantly highly expressed in tumour-infiltrating NK cells, which mediated the dysfunction of tumour-infiltrating NK cells by regulating the IFN-γ/p-STAT1/IRF1 signalling pathway. Knockout of NR4A1 in NK cells not only restored the antitumour function of NK cells but also enhanced the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy. The present findings suggest a regulatory role of NR4A1 in the immune progress of NK cells against HCC, which may provide a new direction for immunotherapies of HCC. © 2022 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
-