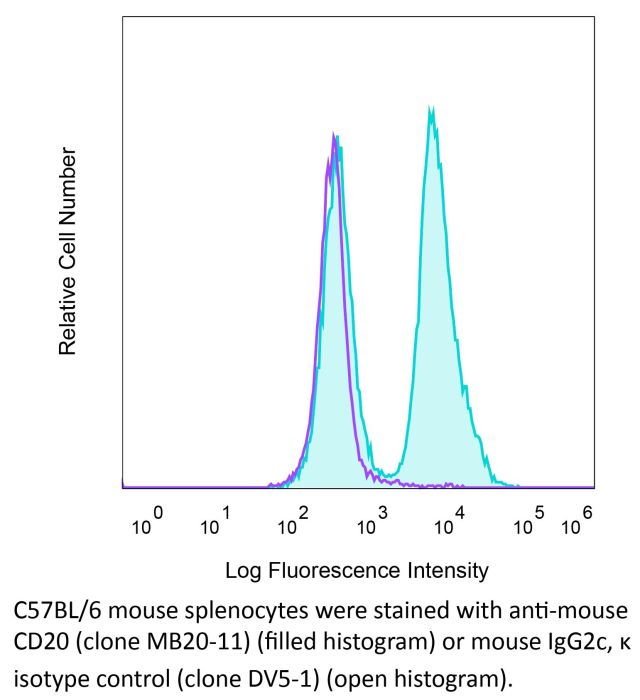
InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD20
Product Description
Bio X Cell is pleased to also offer recombinant MB20-11-CP062. This monoclonal antibody has variable domain sequences identical to MB20-11 but the constant region has been converted from mouse IgG2c to mouse IgG2a for use in mice with the Igh-1a allele. Additionally, the highly controlled sequence and lack of genetic drift in recombinant antibodies provide more reliable and reproducible results over hybridoma derived antibodies.
1: Uchida, Junji et al. “The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through Fc receptor-dependent mechanisms during anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy.” The Journal of experimental medicine vol. 199,12 (2004): 1659-69. doi:10.1084/jem.20040119
2: Xiu, Yan et al. “B lymphocyte depletion by CD20 monoclonal antibody prevents diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice despite isotype-specific differences in Fc gamma R effector functions.” Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) vol. 180,5 (2008): 2863-75. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.2863
3: Hamaguchi, Yasuhito et al. “Antibody isotype-specific engagement of Fcgamma receptors regulates B lymphocyte depletion during CD20 immunotherapy.” The Journal of experimental medicine vol. 203,3 (2006): 743-53. doi:10.1084/jem.20052283
4: Zhang, Zhiping et al. “Possible allelic structure of IgG2a and IgG2c in mice.” Molecular immunology vol. 50,3 (2012): 169-71. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2011.11.006
Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2c, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb mouse IgG2c isotype control, anti-dengue virus |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CD20-GFP transfected 300.19 cells |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo B cell depletion Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2894775 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo B cell depletion
Xiu Y, Wong CP, Bouaziz JD, Hamaguchi Y, Wang Y, Pop SM, Tisch RM, Tedder TF (2008). "B lymphocyte depletion by CD20 monoclonal antibody prevents diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice despite isotype-specific differences in Fc gamma R effector functions
PubMed
NOD mice deficient for B lymphocytes from birth fail to develop autoimmune or type 1 diabetes. To assess whether B cell depletion influences type 1 diabetes in mice with an intact immune system, NOD female mice representing early and late preclinical stages of disease were treated with mouse anti-mouse CD20 mAbs. Short-term CD20 mAb treatment in 5-wk-old NOD female mice reduced B cell numbers by approximately 95%, decreased subsequent insulitis, and prevented diabetes in >60% of littermates. In addition, CD20 mAb treatment of 15-wk-old NOD female mice significantly delayed, but did not prevent, diabetes onset. Protection from diabetes did not result from altered T cell numbers or subset distributions, or regulatory/suppressor T cell generation. Rather, impaired CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation in the lymph nodes of B cell-depleted NOD mice may delay diabetes onset. B cell depletion was achieved despite reduced sensitivity of NOD mice to CD20 mAbs compared with C57BL/6 mice. Decreased B cell depletion resulted from deficient FcgammaRI binding of IgG2a/c CD20 mAbs and 60% reduced spleen monocyte numbers, which in combination reduced Ab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. With high-dose CD20 mAb treatment (250 microg) in NOD mice, FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIV compensated for inadequate FcgammaRI function and mediated B cell depletion. Thereby, NOD mice provide a model for human FcgammaR polymorphisms that reduce therapeutic mAb efficacy in vivo. Moreover, this study defines a new, clinically relevant approach whereby B cell depletion early in the course of disease development may prevent diabetes or delay progression of disease.
in vivo B cell depletion
Xiu Y, Wong CP, Bouaziz JD, Hamaguchi Y, Wang Y, Pop SM, Tisch RM, Tedder TF (2008). "B lymphocyte depletion by CD20 monoclonal antibody prevents diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice despite isotype-specific differences in Fc gamma R effector functions
PubMed
NOD mice deficient for B lymphocytes from birth fail to develop autoimmune or type 1 diabetes. To assess whether B cell depletion influences type 1 diabetes in mice with an intact immune system, NOD female mice representing early and late preclinical stages of disease were treated with mouse anti-mouse CD20 mAbs. Short-term CD20 mAb treatment in 5-wk-old NOD female mice reduced B cell numbers by approximately 95%, decreased subsequent insulitis, and prevented diabetes in >60% of littermates. In addition, CD20 mAb treatment of 15-wk-old NOD female mice significantly delayed, but did not prevent, diabetes onset. Protection from diabetes did not result from altered T cell numbers or subset distributions, or regulatory/suppressor T cell generation. Rather, impaired CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation in the lymph nodes of B cell-depleted NOD mice may delay diabetes onset. B cell depletion was achieved despite reduced sensitivity of NOD mice to CD20 mAbs compared with C57BL/6 mice. Decreased B cell depletion resulted from deficient FcgammaRI binding of IgG2a/c CD20 mAbs and 60% reduced spleen monocyte numbers, which in combination reduced Ab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. With high-dose CD20 mAb treatment (250 microg) in NOD mice, FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIV compensated for inadequate FcgammaRI function and mediated B cell depletion. Thereby, NOD mice provide a model for human FcgammaR polymorphisms that reduce therapeutic mAb efficacy in vivo. Moreover, this study defines a new, clinically relevant approach whereby B cell depletion early in the course of disease development may prevent diabetes or delay progression of disease.
in vivo B cell depletion
Haas, K. M., et al (2010). "Protective and pathogenic roles for B cells during systemic autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice" J Immunol 184(9): 4789-4800.
PubMed
Delineating the relative contributions of B lymphocytes during the course of autoimmune disease has been difficult. Therefore, the effects of depleting all mature B cells using a potent CD20 mAb, or of depleting circulating and marginal zone B cells using a ligand-blocking CD22 mAb, were compared in NZB/W F(1) mice, a model for human systemic lupus erythematosus. Single low-dose mAb treatments depleted B cells efficiently in both NZB/W F(1) and C57BL/6 mice. Prophylactic B cell depletion by repeated CD20 mAb treatments prolonged survival during pristane-accelerated lupus in NZB/W F(1) mice, whereas CD22 mAb had little effect. Despite effective B cell depletion, neither mAb treatment prevented autoantibody generation. In addition, CD20, CD22, and control mAb-treated NZB/W F(1) mice developed anti-mouse IgG autoantibodies in contrast to parental NZB and NZW strains, which may have reduced the effectiveness of B cell depletion. Despite this, low-dose CD20 mAb treatment initiated in 12-28-wk-old mice, and administered every 4 wk thereafter, significantly delayed spontaneous disease in NZB/W F(1) mice. By contrast, B cell depletion initiated in 4-wk-old mice hastened disease onset, which paralleled depletion of the IL-10-producing regulatory B cell subset called B10 cells. B10 cells were phenotypically similar in NZB/W F(1) and C57BL/6 mice, but were expanded significantly in young NZB/W F(1) mice. Thus, B cell depletion had significant effects on NZB/W F(1) mouse survival that were dependent on the timing of treatment initiation. Therefore, distinct B cell populations can have opposing protective and pathogenic roles during lupus progression.
in vivo B cell depletion
Hamaguchi, Y., et al (2006). "Antibody isotype-specific engagement of Fcgamma receptors regulates B lymphocyte depletion during CD20 immunotherapy" J Exp Med 203(3): 743-753.
PubMed
CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb) immunotherapy is effective for lymphoma and autoimmune disease. In a mouse model of immunotherapy using mouse anti-mouse CD20 mAbs, the innate monocyte network depletes B cells through immunoglobulin (Ig)G Fc receptor (FcgammaR)-dependent pathways with a hierarchy of IgG2a/c>IgG1/IgG2b>IgG3. To understand the molecular basis for these CD20 mAb subclass differences, B cell depletion was assessed in mice deficient or blocked for stimulatory FcgammaRI, FcgammaRIII, FcgammaRIV, or FcR common gamma chain, or inhibitory FcgammaRIIB. IgG1 CD20 mAbs induced B cell depletion through preferential, if not exclusive, interactions with low-affinity FcgammaRIII. IgG2b CD20 mAbs interacted preferentially with intermediate affinity FcgammaRIV. The potency of IgG2a/c CD20 mAbs resulted from FcgammaRIV interactions, with potential contributions from high-affinity FcgammaRI. Regardless, FcgammaRIV could mediate IgG2a/b/c CD20 mAb-induced depletion in the absence of FcgammaRI and FcgammaRIII. In contrast, inhibitory FcgammaRIIB deficiency significantly increased CD20 mAb-induced B cell depletion by enhancing monocyte function. Although FcgammaR-dependent pathways regulated B cell depletion from lymphoid tissues, both FcgammaR-dependent and -independent pathways contributed to mature bone marrow and circulating B cell clearance by CD20 mAbs. Thus, isotype-specific mAb interactions with distinct FcgammaRs contribute significantly to the effectiveness of CD20 mAbs in vivo, which may have important clinical implications for CD20 and other mAb-based therapies.
in vivo B cell depletion
Uchida, J., et al (2004). "The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through Fc receptor-dependent mechanisms during anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy" J Exp Med 199(12): 1659-1669.
PubMed
Anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy effectively treats non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and autoimmune disease. However, the cellular and molecular pathways for B cell depletion remain undefined because human mechanistic studies are limited. Proposed mechanisms include antibody-, effector cell-, and complement-dependent cytotoxicity, the disruption of CD20 signaling pathways, and the induction of apoptosis. To identify the mechanisms for B cell depletion in vivo, a new mouse model for anti-CD20 immunotherapy was developed using a panel of twelve mouse anti-mouse CD20 monoclonal antibodies representing all four immunoglobulin G isotypes. Anti-CD20 antibodies rapidly depleted the vast majority of circulating and tissue B cells in an isotype-restricted manner that was completely dependent on effector cell Fc receptor expression. B cell depletion used both FcgammaRI- and FcgammaRIII-dependent pathways, whereas B cells were not eliminated in FcR common gamma chain-deficient mice. Monocytes were the dominant effector cells for B cell depletion, with no demonstrable role for T or natural killer cells. Although most anti-CD20 antibodies activated complement in vitro, B cell depletion was completely effective in mice with genetic deficiencies in C3, C4, or C1q complement components. That the innate monocyte network depletes B cells through FcgammaR-dependent pathways during anti-CD20 immunotherapy has important clinical implications for anti-CD20 and other antibody-based therapies.
in vivo B cell depletion
Uchida, J., et al (2004). "Mouse CD20 expression and function" Int Immunol 16(1): 119-129.
PubMed
CD20 plays a role in human B cell proliferation and is an effective target for immunotherapy. In this study, mouse CD20 expression and biochemistry were assessed for the first time using a new panel of CD20-specific mAb, with CD20 function assessed using CD20-deficient (CD20(-/-)) mice. CD20 expression was B cell restricted and was initiated during late pre-B cell development. The frequency and density of CD20 expression increased during B cell maturation in the bone marrow, with a subpopulation of transitional IgM(hi) B cells expressing higher CD20 levels than the majority of mature recirculating B cells. Transitional T1 B cells in the spleen also expressed high CD20 levels, providing a useful new marker for this B cell subset. In CD20(-/-) mice, immature and mature B cell IgM expression was approximately 20-30% lower relative to B cells from wild-type littermates. In addition, CD19-induced intracellular calcium responses were significantly reduced in CD20(-/-) B cells, with a less dramatic effect on IgM-induced responses. These results reveal a role for CD20 in transmembrane Ca(2+) movement in mouse primary B cells that complements previous results obtained using human CD20 cDNA-transfected cell lines. Otherwise, B cell development, tissue localization, signal transduction, proliferation, T cell-dependent antibody responses and affinity maturation were normal in CD20(-/-) mice. Thus, mouse and human CD20 share similar patterns of expression and function. These studies thereby provide an animal model for studying CD20 function in vivo and the molecular mechanisms that influence anti-CD20 immunotherapy.
in vivo B cell depletion
Haas, K. M., et al (2010). "Protective and pathogenic roles for B cells during systemic autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice" J Immunol 184(9): 4789-4800.
PubMed
Delineating the relative contributions of B lymphocytes during the course of autoimmune disease has been difficult. Therefore, the effects of depleting all mature B cells using a potent CD20 mAb, or of depleting circulating and marginal zone B cells using a ligand-blocking CD22 mAb, were compared in NZB/W F(1) mice, a model for human systemic lupus erythematosus. Single low-dose mAb treatments depleted B cells efficiently in both NZB/W F(1) and C57BL/6 mice. Prophylactic B cell depletion by repeated CD20 mAb treatments prolonged survival during pristane-accelerated lupus in NZB/W F(1) mice, whereas CD22 mAb had little effect. Despite effective B cell depletion, neither mAb treatment prevented autoantibody generation. In addition, CD20, CD22, and control mAb-treated NZB/W F(1) mice developed anti-mouse IgG autoantibodies in contrast to parental NZB and NZW strains, which may have reduced the effectiveness of B cell depletion. Despite this, low-dose CD20 mAb treatment initiated in 12-28-wk-old mice, and administered every 4 wk thereafter, significantly delayed spontaneous disease in NZB/W F(1) mice. By contrast, B cell depletion initiated in 4-wk-old mice hastened disease onset, which paralleled depletion of the IL-10-producing regulatory B cell subset called B10 cells. B10 cells were phenotypically similar in NZB/W F(1) and C57BL/6 mice, but were expanded significantly in young NZB/W F(1) mice. Thus, B cell depletion had significant effects on NZB/W F(1) mouse survival that were dependent on the timing of treatment initiation. Therefore, distinct B cell populations can have opposing protective and pathogenic roles during lupus progression.
in vivo B cell depletion
Hamaguchi, Y., et al (2006). "Antibody isotype-specific engagement of Fcgamma receptors regulates B lymphocyte depletion during CD20 immunotherapy" J Exp Med 203(3): 743-753.
PubMed
CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb) immunotherapy is effective for lymphoma and autoimmune disease. In a mouse model of immunotherapy using mouse anti-mouse CD20 mAbs, the innate monocyte network depletes B cells through immunoglobulin (Ig)G Fc receptor (FcgammaR)-dependent pathways with a hierarchy of IgG2a/c>IgG1/IgG2b>IgG3. To understand the molecular basis for these CD20 mAb subclass differences, B cell depletion was assessed in mice deficient or blocked for stimulatory FcgammaRI, FcgammaRIII, FcgammaRIV, or FcR common gamma chain, or inhibitory FcgammaRIIB. IgG1 CD20 mAbs induced B cell depletion through preferential, if not exclusive, interactions with low-affinity FcgammaRIII. IgG2b CD20 mAbs interacted preferentially with intermediate affinity FcgammaRIV. The potency of IgG2a/c CD20 mAbs resulted from FcgammaRIV interactions, with potential contributions from high-affinity FcgammaRI. Regardless, FcgammaRIV could mediate IgG2a/b/c CD20 mAb-induced depletion in the absence of FcgammaRI and FcgammaRIII. In contrast, inhibitory FcgammaRIIB deficiency significantly increased CD20 mAb-induced B cell depletion by enhancing monocyte function. Although FcgammaR-dependent pathways regulated B cell depletion from lymphoid tissues, both FcgammaR-dependent and -independent pathways contributed to mature bone marrow and circulating B cell clearance by CD20 mAbs. Thus, isotype-specific mAb interactions with distinct FcgammaRs contribute significantly to the effectiveness of CD20 mAbs in vivo, which may have important clinical implications for CD20 and other mAb-based therapies.
in vivo B cell depletion
Uchida, J., et al (2004). "The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through Fc receptor-dependent mechanisms during anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy" J Exp Med 199(12): 1659-1669.
PubMed
Anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy effectively treats non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and autoimmune disease. However, the cellular and molecular pathways for B cell depletion remain undefined because human mechanistic studies are limited. Proposed mechanisms include antibody-, effector cell-, and complement-dependent cytotoxicity, the disruption of CD20 signaling pathways, and the induction of apoptosis. To identify the mechanisms for B cell depletion in vivo, a new mouse model for anti-CD20 immunotherapy was developed using a panel of twelve mouse anti-mouse CD20 monoclonal antibodies representing all four immunoglobulin G isotypes. Anti-CD20 antibodies rapidly depleted the vast majority of circulating and tissue B cells in an isotype-restricted manner that was completely dependent on effector cell Fc receptor expression. B cell depletion used both FcgammaRI- and FcgammaRIII-dependent pathways, whereas B cells were not eliminated in FcR common gamma chain-deficient mice. Monocytes were the dominant effector cells for B cell depletion, with no demonstrable role for T or natural killer cells. Although most anti-CD20 antibodies activated complement in vitro, B cell depletion was completely effective in mice with genetic deficiencies in C3, C4, or C1q complement components. That the innate monocyte network depletes B cells through FcgammaR-dependent pathways during anti-CD20 immunotherapy has important clinical implications for anti-CD20 and other antibody-based therapies.
in vivo B cell depletion
Uchida, J., et al (2004). "Mouse CD20 expression and function" Int Immunol 16(1): 119-129.
PubMed
CD20 plays a role in human B cell proliferation and is an effective target for immunotherapy. In this study, mouse CD20 expression and biochemistry were assessed for the first time using a new panel of CD20-specific mAb, with CD20 function assessed using CD20-deficient (CD20(-/-)) mice. CD20 expression was B cell restricted and was initiated during late pre-B cell development. The frequency and density of CD20 expression increased during B cell maturation in the bone marrow, with a subpopulation of transitional IgM(hi) B cells expressing higher CD20 levels than the majority of mature recirculating B cells. Transitional T1 B cells in the spleen also expressed high CD20 levels, providing a useful new marker for this B cell subset. In CD20(-/-) mice, immature and mature B cell IgM expression was approximately 20-30% lower relative to B cells from wild-type littermates. In addition, CD19-induced intracellular calcium responses were significantly reduced in CD20(-/-) B cells, with a less dramatic effect on IgM-induced responses. These results reveal a role for CD20 in transmembrane Ca(2+) movement in mouse primary B cells that complements previous results obtained using human CD20 cDNA-transfected cell lines. Otherwise, B cell development, tissue localization, signal transduction, proliferation, T cell-dependent antibody responses and affinity maturation were normal in CD20(-/-) mice. Thus, mouse and human CD20 share similar patterns of expression and function. These studies thereby provide an animal model for studying CD20 function in vivo and the molecular mechanisms that influence anti-CD20 immunotherapy.
in vivo B cell depletion
Haas, K. M., et al (2010). "Protective and pathogenic roles for B cells during systemic autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice" J Immunol 184(9): 4789-4800.
PubMed
Delineating the relative contributions of B lymphocytes during the course of autoimmune disease has been difficult. Therefore, the effects of depleting all mature B cells using a potent CD20 mAb, or of depleting circulating and marginal zone B cells using a ligand-blocking CD22 mAb, were compared in NZB/W F(1) mice, a model for human systemic lupus erythematosus. Single low-dose mAb treatments depleted B cells efficiently in both NZB/W F(1) and C57BL/6 mice. Prophylactic B cell depletion by repeated CD20 mAb treatments prolonged survival during pristane-accelerated lupus in NZB/W F(1) mice, whereas CD22 mAb had little effect. Despite effective B cell depletion, neither mAb treatment prevented autoantibody generation. In addition, CD20, CD22, and control mAb-treated NZB/W F(1) mice developed anti-mouse IgG autoantibodies in contrast to parental NZB and NZW strains, which may have reduced the effectiveness of B cell depletion. Despite this, low-dose CD20 mAb treatment initiated in 12-28-wk-old mice, and administered every 4 wk thereafter, significantly delayed spontaneous disease in NZB/W F(1) mice. By contrast, B cell depletion initiated in 4-wk-old mice hastened disease onset, which paralleled depletion of the IL-10-producing regulatory B cell subset called B10 cells. B10 cells were phenotypically similar in NZB/W F(1) and C57BL/6 mice, but were expanded significantly in young NZB/W F(1) mice. Thus, B cell depletion had significant effects on NZB/W F(1) mouse survival that were dependent on the timing of treatment initiation. Therefore, distinct B cell populations can have opposing protective and pathogenic roles during lupus progression.
in vivo B cell depletion
Xiu Y, Wong CP, Bouaziz JD, Hamaguchi Y, Wang Y, Pop SM, Tisch RM, Tedder TF (2008). "B lymphocyte depletion by CD20 monoclonal antibody prevents diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice despite isotype-specific differences in Fc gamma R effector functions
PubMed
NOD mice deficient for B lymphocytes from birth fail to develop autoimmune or type 1 diabetes. To assess whether B cell depletion influences type 1 diabetes in mice with an intact immune system, NOD female mice representing early and late preclinical stages of disease were treated with mouse anti-mouse CD20 mAbs. Short-term CD20 mAb treatment in 5-wk-old NOD female mice reduced B cell numbers by approximately 95%, decreased subsequent insulitis, and prevented diabetes in >60% of littermates. In addition, CD20 mAb treatment of 15-wk-old NOD female mice significantly delayed, but did not prevent, diabetes onset. Protection from diabetes did not result from altered T cell numbers or subset distributions, or regulatory/suppressor T cell generation. Rather, impaired CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation in the lymph nodes of B cell-depleted NOD mice may delay diabetes onset. B cell depletion was achieved despite reduced sensitivity of NOD mice to CD20 mAbs compared with C57BL/6 mice. Decreased B cell depletion resulted from deficient FcgammaRI binding of IgG2a/c CD20 mAbs and 60% reduced spleen monocyte numbers, which in combination reduced Ab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. With high-dose CD20 mAb treatment (250 microg) in NOD mice, FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIV compensated for inadequate FcgammaRI function and mediated B cell depletion. Thereby, NOD mice provide a model for human FcgammaR polymorphisms that reduce therapeutic mAb efficacy in vivo. Moreover, this study defines a new, clinically relevant approach whereby B cell depletion early in the course of disease development may prevent diabetes or delay progression of disease.
in vivo B cell depletion
Hamaguchi, Y., et al (2006). "Antibody isotype-specific engagement of Fcgamma receptors regulates B lymphocyte depletion during CD20 immunotherapy" J Exp Med 203(3): 743-753.
PubMed
CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb) immunotherapy is effective for lymphoma and autoimmune disease. In a mouse model of immunotherapy using mouse anti-mouse CD20 mAbs, the innate monocyte network depletes B cells through immunoglobulin (Ig)G Fc receptor (FcgammaR)-dependent pathways with a hierarchy of IgG2a/c>IgG1/IgG2b>IgG3. To understand the molecular basis for these CD20 mAb subclass differences, B cell depletion was assessed in mice deficient or blocked for stimulatory FcgammaRI, FcgammaRIII, FcgammaRIV, or FcR common gamma chain, or inhibitory FcgammaRIIB. IgG1 CD20 mAbs induced B cell depletion through preferential, if not exclusive, interactions with low-affinity FcgammaRIII. IgG2b CD20 mAbs interacted preferentially with intermediate affinity FcgammaRIV. The potency of IgG2a/c CD20 mAbs resulted from FcgammaRIV interactions, with potential contributions from high-affinity FcgammaRI. Regardless, FcgammaRIV could mediate IgG2a/b/c CD20 mAb-induced depletion in the absence of FcgammaRI and FcgammaRIII. In contrast, inhibitory FcgammaRIIB deficiency significantly increased CD20 mAb-induced B cell depletion by enhancing monocyte function. Although FcgammaR-dependent pathways regulated B cell depletion from lymphoid tissues, both FcgammaR-dependent and -independent pathways contributed to mature bone marrow and circulating B cell clearance by CD20 mAbs. Thus, isotype-specific mAb interactions with distinct FcgammaRs contribute significantly to the effectiveness of CD20 mAbs in vivo, which may have important clinical implications for CD20 and other mAb-based therapies.
in vivo B cell depletion
Uchida, J., et al (2004). "The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through Fc receptor-dependent mechanisms during anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy" J Exp Med 199(12): 1659-1669.
PubMed
Anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy effectively treats non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and autoimmune disease. However, the cellular and molecular pathways for B cell depletion remain undefined because human mechanistic studies are limited. Proposed mechanisms include antibody-, effector cell-, and complement-dependent cytotoxicity, the disruption of CD20 signaling pathways, and the induction of apoptosis. To identify the mechanisms for B cell depletion in vivo, a new mouse model for anti-CD20 immunotherapy was developed using a panel of twelve mouse anti-mouse CD20 monoclonal antibodies representing all four immunoglobulin G isotypes. Anti-CD20 antibodies rapidly depleted the vast majority of circulating and tissue B cells in an isotype-restricted manner that was completely dependent on effector cell Fc receptor expression. B cell depletion used both FcgammaRI- and FcgammaRIII-dependent pathways, whereas B cells were not eliminated in FcR common gamma chain-deficient mice. Monocytes were the dominant effector cells for B cell depletion, with no demonstrable role for T or natural killer cells. Although most anti-CD20 antibodies activated complement in vitro, B cell depletion was completely effective in mice with genetic deficiencies in C3, C4, or C1q complement components. That the innate monocyte network depletes B cells through FcgammaR-dependent pathways during anti-CD20 immunotherapy has important clinical implications for anti-CD20 and other antibody-based therapies.
in vivo B cell depletion
Uchida, J., et al (2004). "Mouse CD20 expression and function" Int Immunol 16(1): 119-129.
PubMed
CD20 plays a role in human B cell proliferation and is an effective target for immunotherapy. In this study, mouse CD20 expression and biochemistry were assessed for the first time using a new panel of CD20-specific mAb, with CD20 function assessed using CD20-deficient (CD20(-/-)) mice. CD20 expression was B cell restricted and was initiated during late pre-B cell development. The frequency and density of CD20 expression increased during B cell maturation in the bone marrow, with a subpopulation of transitional IgM(hi) B cells expressing higher CD20 levels than the majority of mature recirculating B cells. Transitional T1 B cells in the spleen also expressed high CD20 levels, providing a useful new marker for this B cell subset. In CD20(-/-) mice, immature and mature B cell IgM expression was approximately 20-30% lower relative to B cells from wild-type littermates. In addition, CD19-induced intracellular calcium responses were significantly reduced in CD20(-/-) B cells, with a less dramatic effect on IgM-induced responses. These results reveal a role for CD20 in transmembrane Ca(2+) movement in mouse primary B cells that complements previous results obtained using human CD20 cDNA-transfected cell lines. Otherwise, B cell development, tissue localization, signal transduction, proliferation, T cell-dependent antibody responses and affinity maturation were normal in CD20(-/-) mice. Thus, mouse and human CD20 share similar patterns of expression and function. These studies thereby provide an animal model for studying CD20 function in vivo and the molecular mechanisms that influence anti-CD20 immunotherapy.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Natural antibodies drive type 2 immunity in response to damage-associated molecular patterns.
In JCI Insight on 12 March 2024 by Mara, A. B., Rawat, K., et al.
Allergic airway disease (AAD) is an example of type 2 inflammation that leads to chronic airway eosinophilia controlled by CD4 Th2 cells. Inflammation is reinforced by mast cells and basophils armed with allergen-specific IgE made by allergen-specific B2 B cells of the adaptive immune system. Little is known about how AAD is affected by innate B1 cells, which produce natural antibodies (NAbs) that facilitate apoptotic cell clearance and detect damage- and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (DAMPS and PAMPS). We used transgenic mice lacking either B cells or NAbs in distinct mouse models of AAD that require either DAMPS or PAMPS as the initial trigger for type 2 immunity. In a DAMP-induced allergic model, driven by alum and uric acid, mouse strains lacking B cells (CD19DTA), NAbs (IgHEL MD4), or all secreted antibodies (sIgm-/-Aid-/-) displayed a significant reduction in both eosinophilia and Th2 priming compared with WT or Aid-/- mice lacking only germinal center-dependent high-affinity class-switched antibodies. Replenishing B cell-deficient mice with either unimmunized B1 B cells or NAbs during sensitization restored eosinophilia, suggesting that NAbs are required for licensing antigen-presenting cells to prime type 2 immunity. Conversely, PAMP-dependent type 2 priming to house dust mite or Aspergillus was not dependent on NAbs. This study reveals an underappreciated role of B1 B cell-generated NAbs in selectively driving DAMP-induced type 2 immunity.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Engineer a double team of short-lived and glucose-sensing bacteria for cancer eradication.
In Cell Reports Medicine on 20 June 2023 by Jin, Y. & Fu, L.
Rationally designed and engineered bacteria represent an emerging unique approach for cancer treatment. Here, we engineer a short-lived bacterium, mp105, that is effective against diverse cancer types and safe for intravenous administration. We reveal that mp105 combats cancer by direct oncolysis, depletion of tumor-associated macrophages, and elicitation of CD4+ T cell immunity. We further engineer a glucose-sensing bacterium named m6001 that selectively colonizes solid tumors. When intratumorally injected, m6001 clears tumors more efficiently than mp105 due to its post-delivery replication in tumors and potent oncolytic capacity. Finally, we combine intravenous injection of mp105 and intratumoral injection of m6001, forming a double team against cancer. The double team enhances cancer therapy compared with single treatment for subjects carrying both intratumorally injectable and uninjectable tumors. The two anticancer bacteria and their combination are applicable to different scenarios, turning bacterial therapy for cancer into a feasible solution. Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Profiling of syngeneic mouse HCC tumor models as a framework to understand anti-PD-1 sensitive tumor microenvironments.
In Hepatology on 1 May 2023 by Zabransky, D. J., Danilova, L., et al.
The treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been transformed by the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, most patients with HCC do not benefit from treatment with immunotherapy. There is an urgent need to understand the mechanisms that underlie response or resistance to immunotherapy for patients with HCC. The use of syngeneic mouse models that closely recapitulate the heterogeneity of human HCC will provide opportunities to examine the complex interactions between cancer cells and nonmalignant cells in the tumor microenvironment. We leverage a multifaceted approach that includes imaging mass cytometry and suspension cytometry by time of flight to profile the tumor microenvironments of the Hep53.4, Hepa 1-6, RIL-175, and TIBx (derivative of TIB-75) syngeneic mouse HCC models. The immune tumor microenvironments vary across these four models, and various immunosuppressive pathways exist at baseline in orthotopic liver tumors derived from these models. For instance, TIBx, which is resistant to anti-programmed cell death protein 1 therapy, contains a high proportion of "M2-like" tumor-associated macrophages with the potential to diminish antitumor immunity. Investigation of The Cancer Genome Atlas reveals that the baseline immunologic profiles of Hep53.4, RIL-175, and TIBx are broadly representative of human HCCs; however, Hepa 1-6 does not recapitulate the immune tumor microenvironment of the vast majority of human HCCs. There is a wide diversity in the immune tumor microenvironments in preclinical models and in human HCC, highlighting the need to use multiple syngeneic HCC models to improve the understanding of how to treat HCC through immune modulation. Copyright © 2023 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Balance between immunoregulatory B cells and plasma cells drives pancreatic tumor immunity.
In Cell Reports Medicine on 20 September 2022 by Mirlekar, B., Wang, Y., et al.
Plasma cell responses are associated with anti-tumor immunity and favorable response to immunotherapy. B cells can amplify anti-tumor immune responses through antibody production; yet B cells in patients and tumor-bearing mice often fail to support this effector function. We identify dysregulated transcriptional program in B cells that disrupts differentiation of naive B cells into anti-tumor plasma cells. The signaling network contributing to this dysfunction is driven by interleukin (IL) 35 stimulation of a STAT3-PAX5 complex that upregulates the transcriptional regulator BCL6 in naive B cells. Transient inhibition of BCL6 in tumor-educated naive B cells is sufficient to reverse the dysfunction in B cell differentiation, stimulating the intra-tumoral accumulation of plasma cells and effector T cells and rendering pancreatic tumors sensitive to anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade. Our findings argue that B cell effector dysfunction in cancer can be due to an active systemic suppression program that can be targeted to synergize with T cell-directed immunotherapy.Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-